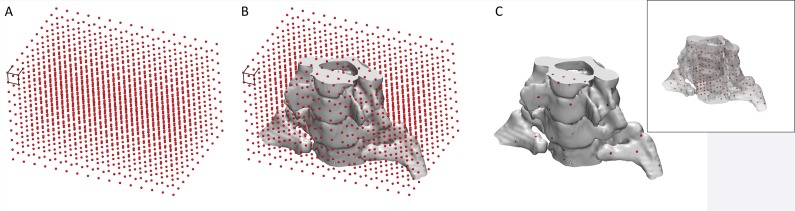
Figure 9.
Conceptual illustration of the use of internal fiduciary markers to establish the dimensional accuracy of a 3D printed model. A, A grid of markers—0.7-mm–diameter spheres with 7-mm spacing between them—covers, B, the extent of the model. C, Markers that fall within the solid part of the model and made of material that has similar mechanical properties but different radiodensity compared with the remainder of the model can be printed. An image of the model with different marker radiodensity compared with the radiodensity of the remainder of the model can be used to extract coordinates of the markers and compare these coordinates with locations on the designed grid to establish the dimensional accuracy of the model. Inset: All markers within the model can be seen because the model is plotted as a semitransparent object.