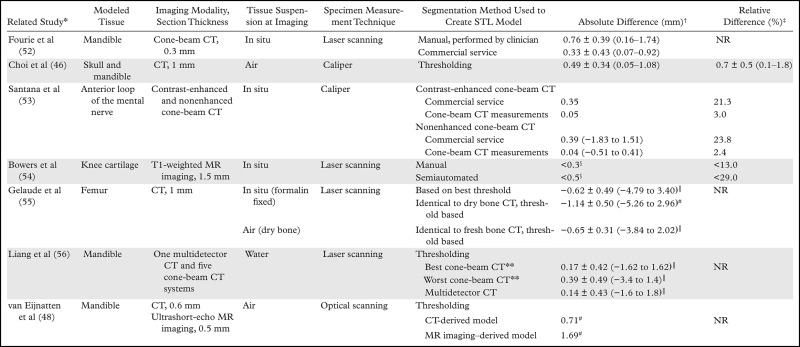
Table 4:
Reported Accuracies of STL Bone Models, as Compared with Cadaveric Specimens
*Numbers in parentheses are corresponding reference numbers.
†Absolute differences (imaging and segmentation errors) between the segmentation-generated STL model and cadaveric specimen, cited as mean values or means ± standard deviations, with ranges in parentheses, unless otherwise noted.
‡Mean relative differences (imaging and segmentation errors) between the segmentation-generated STL model and cadaveric specimen. Data from the Choi et al study (46) are the mean relative difference ± the standard deviation, with the range in parentheses. Data from the Bowers et al (54) study are maximal relative differences. NR = not reported.
§Approximate maximal absolute difference values.
║Average signed differences. Negative values indicate that the STL model was larger than the cadaveric specimen.
#Ninety-fifth percentile of signed (with positive and negative differences, as opposed to the absolute difference, considered) differences.
**Liang et al (56) used five cone-beam CT systems. The absolute difference values of the systems that demonstrated the best and worst accuracy are reported.