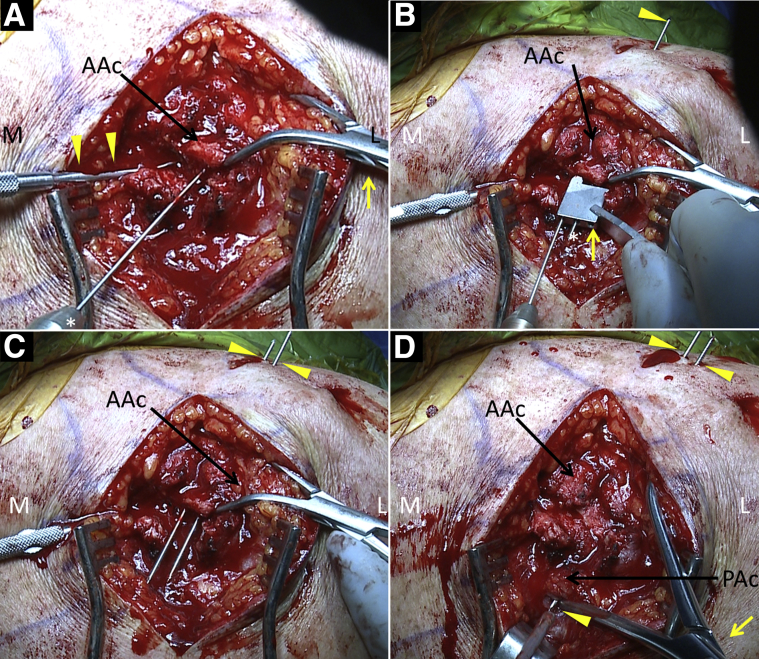
Fig 4.
Right shoulder from a posterior view. (A) While the anterior acromion (AAc) is held in place by a reduction clamp (yellow arrow) and freer elevator (arrowheads), using a drill (*), a K-wire is advanced anteriorly through the posterior aspect of the anterior fragment of the acromion and (B) out the anterior skin (arrowhead); a drill guide (yellow arrow) is then placed over the first K-wire to allow the second K-wire (*) to be placed parallel to and at a fixed distance away from the first. (C) The K-wires (arrowheads) are advanced anteriorly. (D) The os acromiale is reduced into desired position with the reduction clamp (yellow arrow); the K-wires (arrowheads) are then drilled posteriorly into the posterior acromion, providing provisional fixation. (AAc, anterior acromion; L, lateral; M, medial; PAc, posterior acromion.)