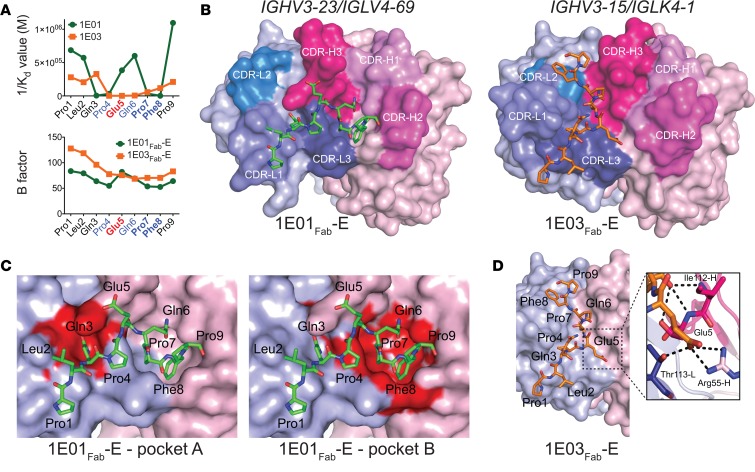
Figure 2. Recognition of the peptide PLQPEQPFP by IGHV3-23/IGLV4-69 and IGHV3-15/IGKV4-1 hmAbs.
(A) Binding (1/Kd values determined by MST) of hmAbs 1E01 (IGHV3-23/IGLV4-69) and 1E03 (IGHV3-15/IGKV4-1) to Ala-substituted variants of the DGP (upper panel), and B-factor distribution for the cocrystal structures 1E01Fab-E and 1E03Fab-E (lower panel). Residues predicted to be involved in substrate recognition by TG2 are shown in blue, with residues being particularly important in bold. The Glu5 residue formed by TG2-mediated deamidation is shown in red. (B) Docking of DGP to structures of 1E01Fab and 1E03Fab. (C) Two pockets in the surface of 1E01Fab-E accommodate side chains of peptide residues Gln3 (pocket A) and Pro7/Phe8 (pocket B). (D) The interaction surface of 1E03Fab-E displays no major pockets for harboring side chains of DGP residues. In the zoom-in, bonds between Glu5 of the peptide and with R55-H (salt bridge) and T113-L (hydrogen bond) are shown as black dotted lines. Interacting residues are drawn as sticks, with nitrogen atoms in blue and oxygen atoms in red.