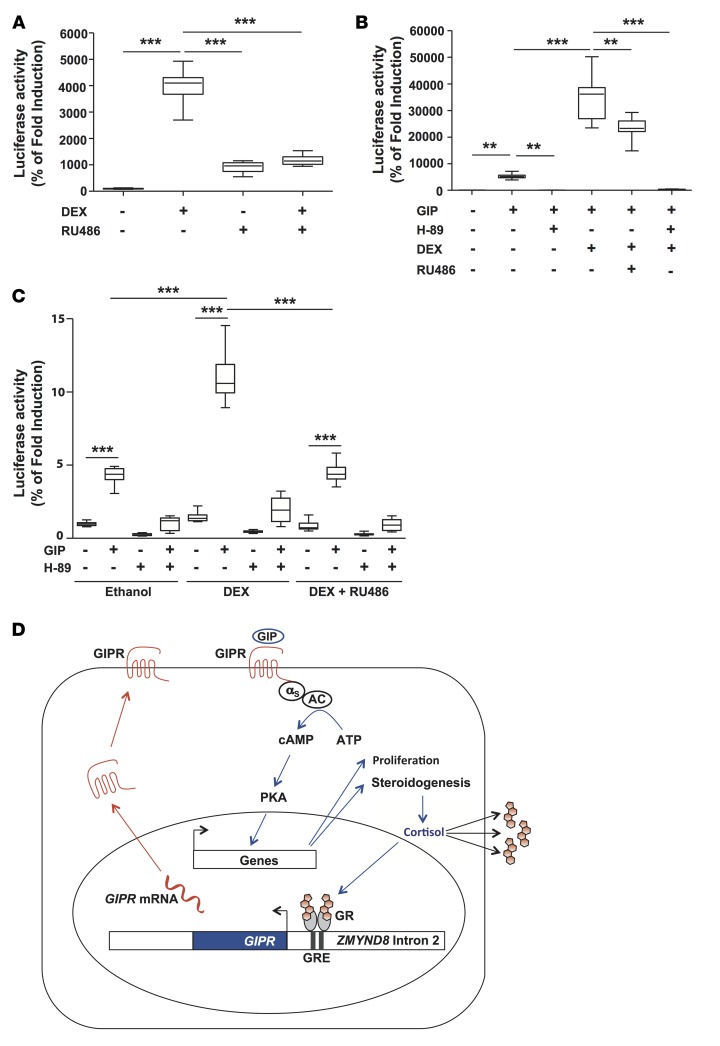
Figure 4. Functional analysis of zinc finger and MYND (myeloid, Nervy, and DEAF-1) domain containing 8 (ZMYND8) intron 2–glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) chromosome rearrangement.
(A) Transient transfection assays of HEK 293T cells with a ZMYND8 intron 2-pGL4.26-Luciferase vector (Supplemental Figure 5A). Transactivation of ZMYND8 intron 2 by dexamethasone (DEX), and its prevention by the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist RU486, confirms the functional status of the glucocorticoid response element (GRE) in ZMYND8 intron 2. Transient transfection assays of HEK 293T cells (B) and adrenocortical H295R cells (C) with a chimeric ZMYND8 intron 2–pGL4.26–GIPR plasmid (Supplemental Figure 5B) and a CRE-Luc reporter vector. Treatment with glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) resulted in increased cAMP signaling, as shown by transactivation of the cAMP response elements (CRE) in the CRE-Luc vector, indicating that transfected cells expressed functional GIPR. Co-treatment with dexamethasone resulted in a significant increase in GIP-induced cAMP production, demonstrating enhancement of GIPR expression by glucocorticoids. Data in A–C are presented as box-and-whisker plots. The bounds of the boxes represent the first and the third quartiles (bottom and top of the box); the lines within the boxes represent the median values; the whiskers depict the minimal and maximal values. Presented data are the means of 2 independent experiments, with n = 8 for each experiment. Statistical significance was evaluated by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post-test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (D) Schematic representation of the positive regulatory loop that maintains ectopic GIPR expression in the adenoma of patient #1.