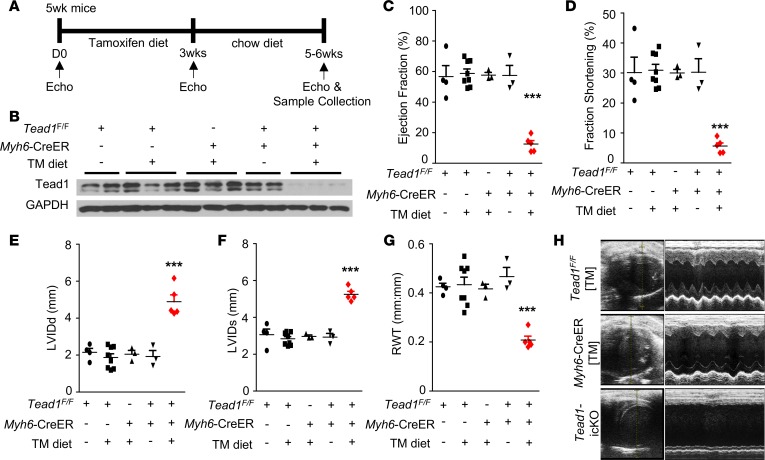
Figure 1. Tead1 ablation in adult cardiomyocytes leads to acute diminished cardiac contractility.
(A) Experimental procedure and tamoxifen diet protocol for inducing CM-specific Tead1 KO (Tead1-icKO). (B) Tead1 protein expression in the heart ventricles. GAPDH, loading control. TM, tamoxifen. (C) Ejection fraction, (D) fractional shortening, (E) left ventricular internal diameter at end diastole (LVIDd), (F) left ventricular internal diameter at end systole (LVIDs), and (G) relative wall thickness (RWT) by echocardiography (Echo) at 6 weeks after starting TM diet. Values are shown as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001; data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. Comparisons between Tead1-icKO mice (n = 6–8) and TeadF/F chow diet mice (n = 4), TeadF/F TM diet mice (n = 8), Myh6-CreER TM diet mice (n = 3), or TeadF/F;Myh6-CreER chow diet mice (n = 3) were statistically significant. No significance was present among the four control groups. (H) Representative 2-D M-mode images of the left ventricle from Echo assessment of the TeadF/F TM diet, Myh6-CreER TM diet, and Tead1-icKO mice at 6 weeks after starting TM diet.