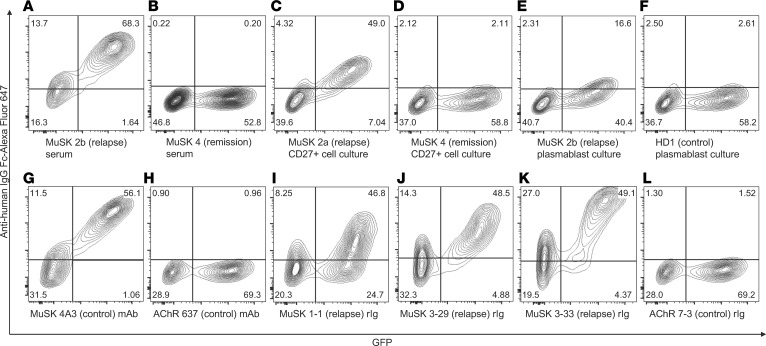
Figure 1. Representative MuSK cell-based assay (CBA) flow cytometry plots.
Control sera, cell culture supernatants, and monoclonal rIgs were tested for surface binding to MuSK on MuSK-GFP–transfected HEK cells. The x axis represents GFP fluorescence intensity and, consequently, the fraction of HEK cells transfected with MuSK. The y axis represents Alexa Fluor 647 fluorescence intensity, which corresponds to secondary anti–human IgG Fc antibody binding and, consequently, primary antibody binding to MuSK. Hence, transfected cells are located in the right quadrants and cells with MuSK autoantibody binding in the upper quadrants. The upper right quadrant shows cells that are both transfected with MuSK-GFP and that bind MuSK autoantibodies, whereas the upper left quadrant represents nonspecific antibody binding to HEK cell antigens. All results shown were reproduced in duplicate experiments. (A–F) Serum and B cell culture supernatants; (G–L) monoclonal rIg. (A) Post–rituximab relapse (MuSK 2b) serum; (B) post–rituximab remission (MuSK 4) serum; (C) post–rituximab relapse (MuSK 2a) CD27+ B cell culture supernatant; (D) post–rituximab remission (MuSK 4) CD27+ B cell culture supernatant; (E) post–rituximab relapse (MuSK 2b) plasmablast culture supernatant; (F) post–viral URI (HD 1) plasmablast culture supernatant; (G) 4A3, a humanized murine MuSK–specific monoclonal rIg; (H) 637, a human AChR–specific monoclonal rIg; (I) post–rituximab relapse (MuSK 1) PB–derived rIg 1-1; (J) post–rituximab relapse (MuSK 3) PB–derived rIg 3-29; (K) post–rituximab relapse (MuSK 3) PB–derived rIg 3-33; (L) AChR MG (AChR 7) PB–derived rIg 7-3. AChR, acetylcholine receptor; HD, healthy donor; HEK, human embryonic kidney; MuSK, muscle-specific tyrosine kinase; rIg, recombinant Ig; URI, upper respiratory tract infection.