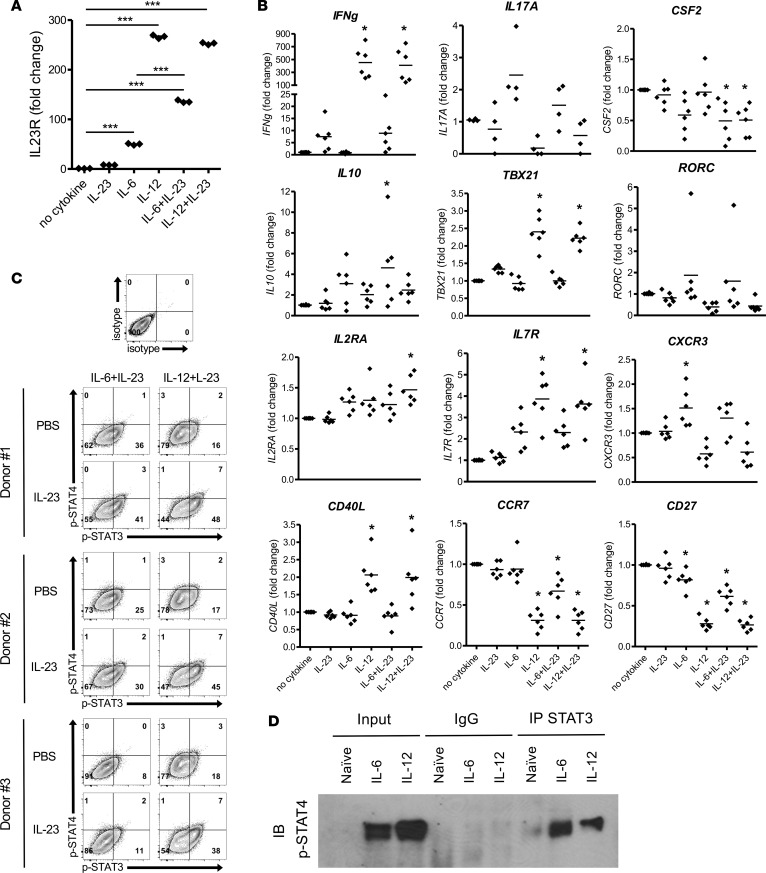
Figure 6. IL-23R signals through p-STAT3/p-STAT4 heterodimers on human CD4+ T cells differentiated IL-6 or IL-12.
Naive human CD4+ T cells were purified from PBMCs of healthy donors and activated in vitro with anti-CD3/CD28–coated beads in the presence of IL-23, IL-6, IL-12, or combinations. (A) Cells were collected at 48 hours, and IL-23R and HPRT mRNA were detected by real-time PCR. Fold change of gene expression was shown relative to no cytokine condition (mean ± SEM). ***P < 0.001 (1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). (B) Additional genes were analyzed by real-time PCR (n = 6 healthy donors). *P < 0.05 (1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). (C) At 72 hours, the activated T cells were washed and rested in fresh medium for 4 hours, and then IL-23 or PBS were added as secondary stimulations. After 20 minutes, phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT4 in CD4+ T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) After 30 minutes, differentiated cells were collected, and undifferentiated naive CD4+ T cells from the same donor served as a negative control. Nuclear protein was extracted for use in a co-IP assay performed with Ab for total STAT3 or nonspecific mouse IgG. Precipitated protein complexes and inputs were electrophoresed with SDS-PAGE. p-STAT4 was detected by Western blot. Data is representative of at least 2 independent experiments.