Figure 7.
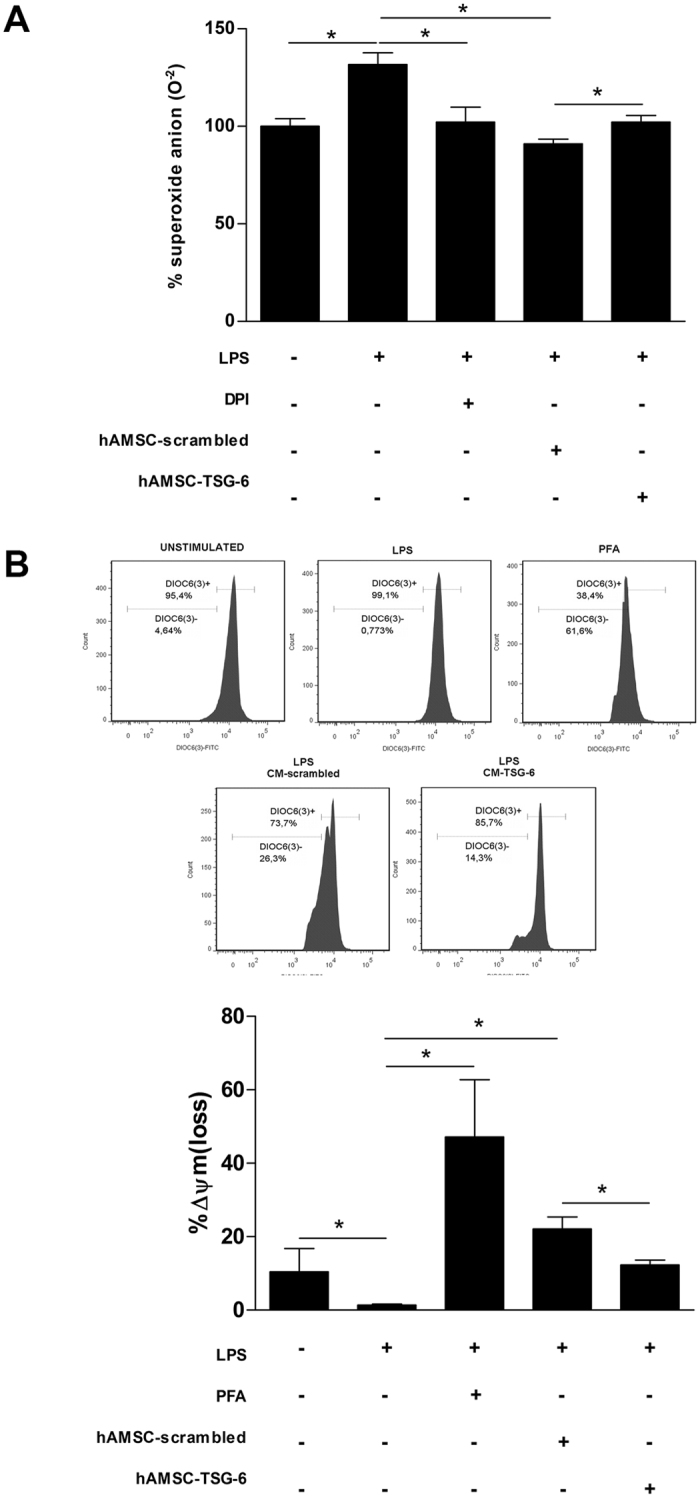
The decrease of NETs release through TSG-6 is ROS dependent. Murine neutrophils were stimulated with LPS and incubated with the CM-hAMSC-scrambled or CM-hAMSC-TSG-6 during 30 min. The siRNA-scrambled was used to corroborate that the specific silencing of TSG-6, did not affect the immunosuppressive effect of CM from hAMSC. The ROS production was determined with the NBT reduction assay. Data are expressed as the percentage of superoxide anion production. Graphic of percentage of superoxide anion production in LPS-stimulated neutrophils cultured with the CM-hAMSC scrambled or CM-hAMSC-TSG-6. Bars represent the mean percentage of superoxide anion ± SD (n = 3), *p < 0.05 (unstimulated vs. LPS; LPS vs. DPI; LPS vs. CM-hAMSC-scrambled; CM-hAMSC-scrambled vs. CM-hAMSC-TSG-6). DPI (Diphenyleneiodonium) an inhibitor of NADPH complex was used as inhibitor of ROS and superoxide anion production (A). The mitochondrial membrane potential was measured with the fluorescent dye DiOC6(3) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as the percentage of Δψm loss. Graphic of the percentage of Δψm loss of LPS-stimulated neutrophils cultured with the CM-hAMSC-scrambled or CM-hAMSC-TSG-6. The percentage of Δψm loss of LPS-stimulated neutrophils cultured with the CM-hAMSC-scrambled increased with respect to LPS-stimulated neutrophils only with fresh medium or cultured in the presence of CM-hAMSC-TSG-6. p-formaldehyde (PFA) treated LPS-stimulated neutrophils were used as a positive control of the Δψm loss. Bars represent the mean percentage of Δψm loss ± SD (n = 3), *p < 0.05 (unstimulated vs. LPS; LPS vs. PFA; LPS vs. CM-hAMSC-scrambled; CM-hAMSC-scrambled vs. CM-hAMSC-TSG-6 (B).
