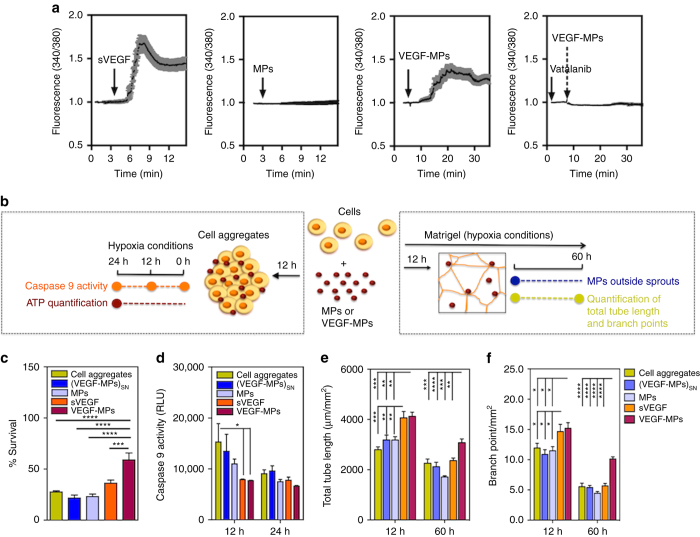
Fig. 2.
The biological effect of VEGF-MPs on OEPCs. a Single cell calcium measurements. OEPCs were starved in medium without serum for 20 h, loaded with a Ca2+ probe and activated by VEGF, blank MPs, VEGF-MPs, or inhibited by Vatalanib, an inhibitor of VEGFR-2. The arrows indicate the time when the compounds or MPs were added. At least 10 cells have been monitored for intracellular Ca2+ in each of the experimental groups. Averages and SEM values are in black and grey, respectively. b Schematic representation of the protocols used to demonstrate the higher OEPC survival and activity after exposure to VEGF-MPs than sVEGF. c, d The survival (c 24 h) and apoptosis (d 12 and 24 h) of OEPCs in aggregates under hypoxia in serum-deprived conditions as assessed by an ATP-based assay or the measurement of caspase 9 activity. e, f OEPC aggregates were cultured on Matrigel under hypoxia for 12 and 60 h, after which the tube length (e) and branching points (f) were measured. MPs indicate cell aggregates containing uncoated beads while (VEGF-MPs)SN indicates cell aggregates exposed to the supernatant of VEGF-MPs. In all graphs, values are given as average ± SEM (n = 3–8). Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001