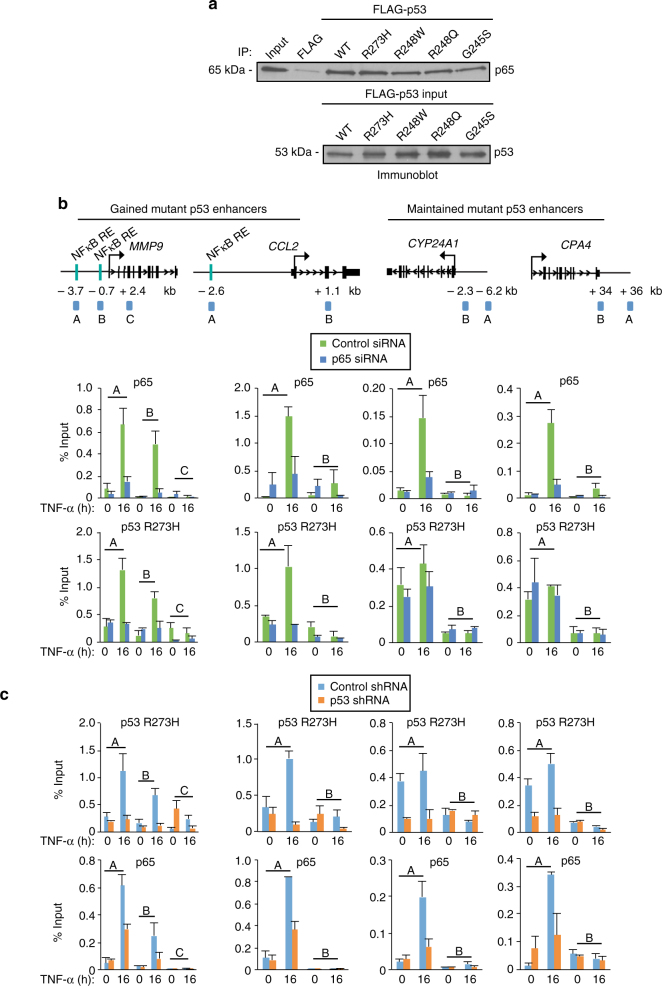
Fig. 3.
Mutp53 and NFκB interact and impact each other’s binding at enhancers. a Purified wild-type and mutp53 proteins bind directly to purified NFκB/p65 as revealed by immunoblot analysis with an antibody that recognizes p65. Input samples for the p53 proteins were also analyzed by immunoblot analysis with an antibody that recognizes both wild-type and mutp53. Three independent interaction assays were performed. b ChIP-qPCR analyses of NFκB/p65 and p53 R273H at the enhancer (A and B at MMP9 and A at CCL2, CYP24A1, and CPA4) or non-specific (C at MMP9 and B at CCL2, CYP24A1, and CPA4) regions of the target gene loci in SW480 cells transfected with non-targeting control or p65 siRNA and following TNF-α treatment for 0 or 16 h. c ChIP-qPCR analyses of p53 R273H and NFκB/p65 binding at identical genomic regions examined in (b). The SW480 cells were induced to express LacZ (control) or p53 (p53) shRNA and treated with TNF-α for 0 or 16 h. For both ChIP experiments, an average of two independent experiments that are representative of at least three is shown with error bars denoting the standard error