Fig. 1.
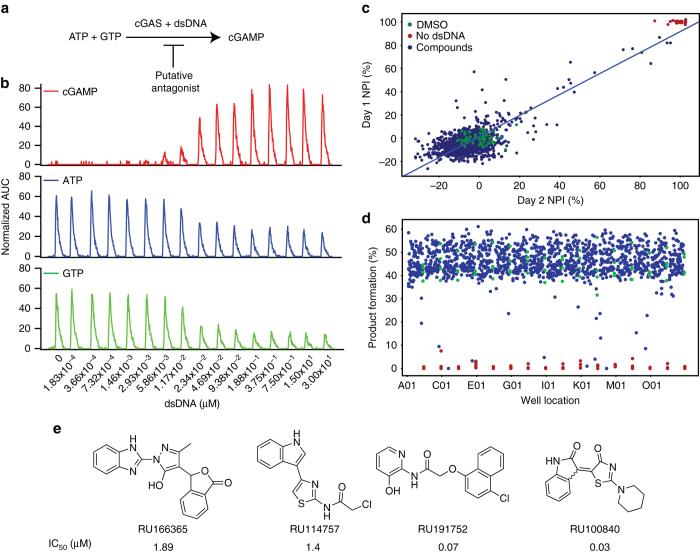
Development of a high-throughput screen for the identification of cGAS inhibitors. a Schematic of immune stimulatory dsDNA-dependent cGAS synthesis of cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP). b The enzymatic activity of cGAS is determined by monitoring the consumption of ATP (blue) and GTP (green), and the generation of cGAMP (red) using an RF-MS. The assay was incubated for 120 min using 60 nM cGAS. Normalized extracted ion count values are plotted. c For the high-throughput screen, 300 nM dsDNA was used to stimulate mouse cGAS activity; % cGAMP product formation was measured against 1266 compounds (blue dots) at a final concentration of 12.5 μM using Sigma-Aldrich LOPAC (library of pharmacologically active compound) library plates. The results of two independent days, as technical replicates, are plotted against each other as normalized percent of inhibition (NPI). The negative control DMSO is shown in green and the positive control (no dsDNA) is shown in red. Data were analyzed using Vortex software and the coefficient of correlation was 0.86. d The results using the LOPAC library resulted in the assay having a Z prime factor of 0.76. e Following the high-throughput screen from over 100,000 small-molecule compounds, the following four were selected for additional characterization. See text for details on the triage process