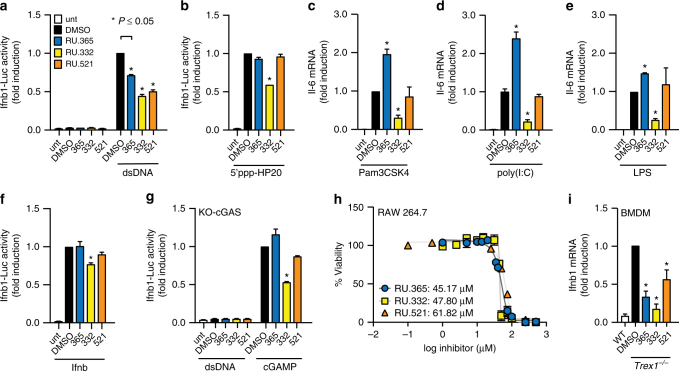
Fig. 6.
Potent and selective inhibition of cGAS activity in RAW macrophage and BMDM cells from an Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome mouse model. RAW luciferase reporter cells were exposed to dsDNA (a), 5′ppp-HP20 RNA (b), Pam3CSK4 (c), poly(I:C) (d), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (e), or recombinant murine interferon-β (Ifnb) f to promote either a type I interferon (a), (b), (f), or NF-κB (c), (d), (e) response under different immune stimuli and simultaneously treated with indicated small molecule (or vehicle). Type I interferon response was read via luciferase reporter, while NF-κB response was read via qRT-PCR. g RAW KO-cGAS reporter cells were exposed to dsDNA or cGAMP and simultaneously treated with each of the small molecules. h The cytotoxic effects of the lead compounds were tested in RAW macrophages at concentrations spanning the range tested in the dose response curves. Cytotoxicity was measured by the quantitation of ATP (CellTiter-Glo assay) at 72 h and shown as percent viability of cells. i BMDM cells from Trex1 −/− mice were treated with the indicated compound for 24 h and then harvested for qRT-PCR analysis. Shown are the results, relative to IFNB1 expression in Trex1 wild-type BMDMs. Error bars represent SEM