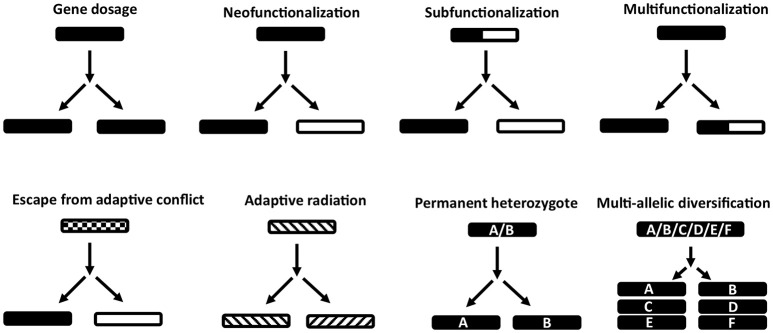
Figure 2.
Models of gene duplication and evolution of function. Indicated are various models for the evolution of function before and after gene duplication events. Gene dosage refers to maintenance of gene duplicates with the same function. Neofunctionalization refers to the acquisition of a new function and loss of the old function in one gene duplicate. Subfunctionalization refers to the segregation of two functions in different gene duplicates that was present in the ancestral gene. Multifunctionalization refers to acquisition of a new function in one gene copy, while retaining the original function. Escape from adaptive conflict refers to an ancestral gene with functions that are overlapping or sub-functional due to exclusion effects. These functions are optimized in respective gene duplicates after duplication. Adaptive radiation refers to ancestral genes that have pre-adapted functions, which allow the evolution of similar functions in gene duplicates. Permanent heterozygote refers to heterozygotes that have better fitness than homozygotes and where gene duplication leads to fixation of both alleles in paralogs. Multi-allelic diversification refers to the case where the highest number of heterozygous individuals in a population is advantageous. Gene duplications leads to many divergent genes coding for the same function.