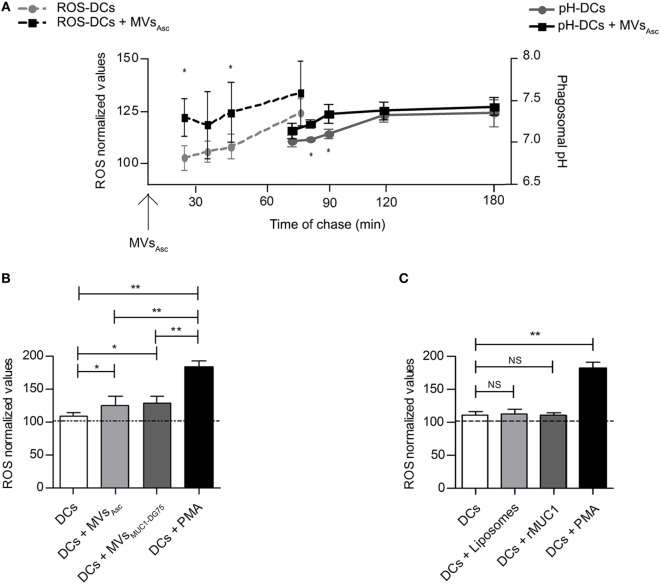
Figure 3.
Phagosomal reactive oxygen species (ROS) molecules increase following dendritic cell (DC) uptake of tumor microvesicles (MVs) shortly before phagosomal alkalinization. (A) Modulation of the phagosomal ROS (dotted lines) and pH (continuous lines) in DCs following internalization of MVsAsc considered as T0 for both the kinetic measurements. Results are plotted as average of 4 independent experiments for ROS analysis and 5 independent experiments for phagosomal pH analysis. SD and statistical significance are also shown (*p < 0.05). (B) ROS measurement at 30 min of chase; MV pulsed DCs (light and dark gray histograms for DCs + MVsAsc and DCs + MVsDG75-MUC1 samples, respectively) had a significant higher ROS content compared to unpulsed DCs (white histogram, *p < 0.05). PMA-treated DCs (black histogram) are used as positive control. ROS levels are plotted as arbitrary units of three independent experiments (three donors) normalized toward the unpulsed DCs at time 0 of chase (100 arbitrary units). (C) ROS measurement at 30 min of chase; DCs pulsed with Liposomes (light gray histogram) and with the soluble recombinant MUC1 glycoprotein (rMUC1) glycoprotein (dark gray histogram) did not show any difference in term of ROS content compared to unpulsed DCs (white histogram). PMA-treated DCs (black histogram) were used as positive control. ROS levels are plotted as arbitrary units of three independent experiments (three donors). ROS level in unpulsed DCs at time 0 of chase correspond to 100 arbitrary units (dotted line). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.