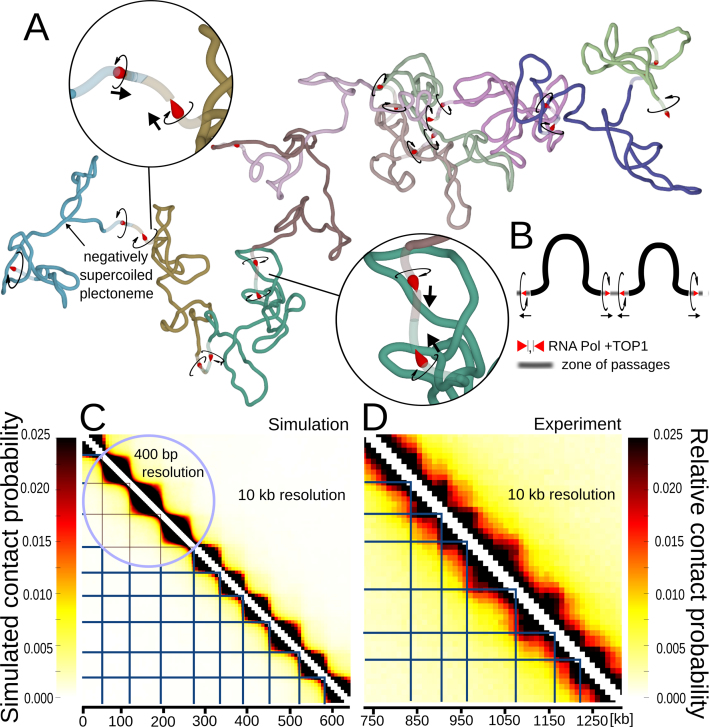
Figure 2.
Simulations of large chromosome fragments with 10 divergent transcription domains separated by sites where torsional stress gets dissipated and zones where portions of modelled chains can pass through each other. (A) Simulation snapshot. Each domain with divergent transcription is marked with a different colour. Torsional motors and swivel sites are presented as in Figure 1A–C. The zones where portions of the chain can pass through each other are presented as semi-transparent. (B) Schematic linear map of two consecutive domains showing the location of modelled RNA polymerases with TOP1 preceding them and also showing location of zones of passages. Circular arrows indicate the direction of rotation induced by respective polymerases. Normal arrows indicate the direction of transcription. (C) Contact map obtained upon analysis of nearly 20 millions of configurations of modelled chromosome fragments such as shown in A. Notice that each of the modelled divergent transcription domains forms a TAD-like region with increased frequency of internal contacts. The blue horizontal and vertical lines indicate positions of gene convergence imposed in our model. (D) Experimental contact map of a portion of S. pombe chromosome with 10 divergent transcription domains. This contact map was obtained using experimental data deposited by Mizuguchi et al. (11) and corresponds to the portion of chromosome 2 ranging from ∼750 to 1300 kb positions of that chromosome. The blue horizontal and vertical lines indicate positions of local maxima of gene convergence in the corresponding chromosome fragment as determined by Mizuguchi et al. (11). Notice that the sizes of self-interacting domains in the modelled chromosome fragment (A and C), reflect the distribution of self-interacting domain sizes observed in all S. pombe chromosomes and were not adjusted to fit the sizes of self-interacting domains in the chromosome fragment, whose contact map is shown in C.