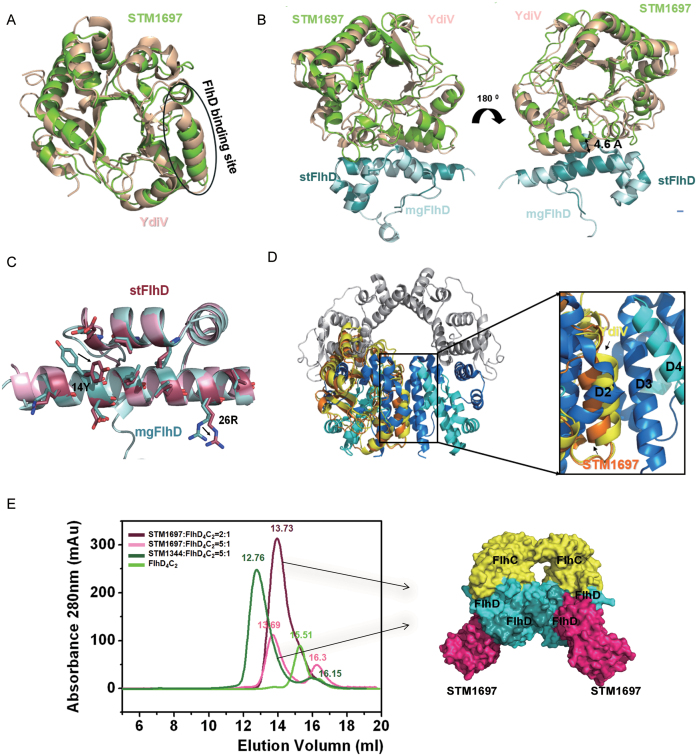
Figure 4.
Structural comparison of STM1697–stFlhD and YdiV–mgFlhD. (A) Structural superposition of STM1697 and YdiV. The two structures are shown in cartoon mode (YdiV: light yellow, STM1697: green). The FlhD binding sites for STM1697 and YdiV are indicated by circles. (B) Structural superposition of STM1697–stFlhD and YdiV–FlhD. The stFlhD in the STM1697–stFlhD structure is used as the reference structure and YdiV-FlhD is superimposed onto the STM1697–stFlhD complex (stFlhD: blue, mgFlhD: light blue, YdiV: light yellow, STM1697: green). (C) Details of changes in the stFlhD and mgFlhD (stFlhD from Salmonella typhimurium, mgFlhD from Escherichia coli MG1655) in the complex structure. Residues located in the interface are shown in stick mode with different colors (stFlhD: hotpink, mgFlhD: blue). The positional changes of the side-chains of 14Y and 26R are indicated by arrows. (D) The structure of FlhD4C2 is used as a model, and STM1697–stFlhD and YdiV–FlhD are separately superimposed onto the third FlhD molecule of FlhD4C2 (STM1697: orange, YdiV: yellow, FlhD: blue). Whole structures are shown in cartoon mode. The right figure presents a close-up view of the interface between the second and the third FlhD molecules of FlhD4C2. All interfaces are overlapped, and the interface of YdiV–FlhD shows more interactions than STM1697–stFlhD and D2–D3. (E) STM1697 and FlhD4C2 cannot form the (STM1697)4 FlhD4C2 hetero-decamer. Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) results of the 2:1 and 5:1 mixtures of STM1697 and FlhD4C2. The STM1344 and FlhD4C2 mixture is used as a positive control because it forms the (STM1344)4 FlhD4C2 hetero-decamer in vitro. FlhD4C2 alone is used as another control. The elution volume of every peak value is marked in the corresponding colors. STM16972FlhD4C2 complex appeared in solution, but no hetero-decamer formed when the ratio of STM1697 and FlhD4C2 reached 5:1. The right figure presents the model of the STM16972FlhD4C2 hetero-hexamer.