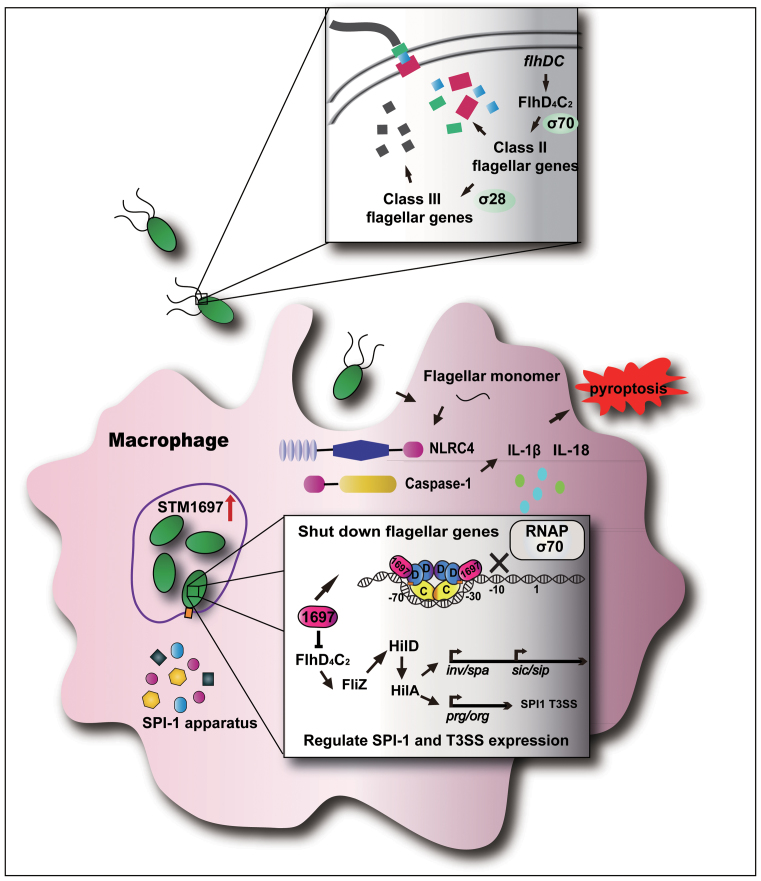
Figure 8.
The role of STM1697 in the Salmonella infection process. Before entry into the host cell, the expression of STM1697 remains at a low level. FlhD4C2 complex binds to the upstream region of flagellar genes and recruits RNA polymerase to express flagellar genes. When Salmonella enters the host cell, the expression of STM1697 is stimulated by some unknown mechanism. STM1697 then binds to the peripheral FlhD of the FlhD4C2 complex, which restrains the recruitment of RNA polymerase by steric exclusion. As a result, the expression of flagellar genes is repressed, and then the expression of FliZ-regulated genes is also downregulated. Salmonella benefits from this process to escape the host immune system.