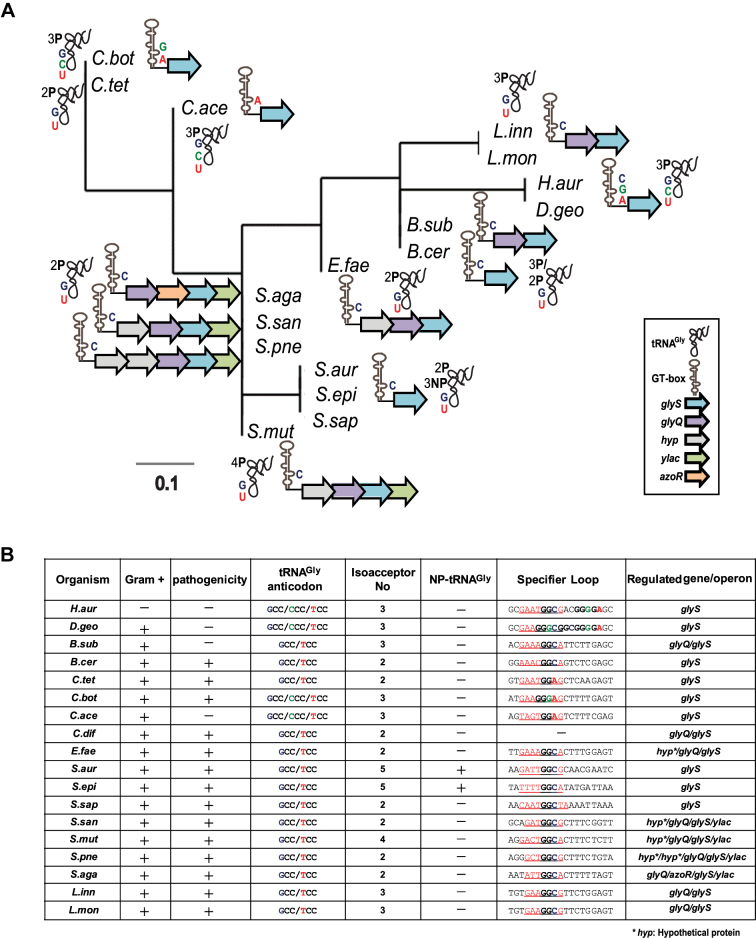
Figure 1.
(A) Phylogenetic tree constructed after analysis of the predicted GT-boxes based on the mRNA leader region from the SL until the T-box conserved sequence, along with the SL specificity (indicated with C for the GGC triplet, A for the GGA and G for the GGG) and the tRNAGly isoacceptor specificity. The number of proteinogenic (P) and non-proteinogenic (NP) isoacceptors and their corresponding anticodon triplet is shown (G for GCC, U for UCC, and C for CCC). (B) GT-boxes distribution among different pathogens, the potential SL regions and the tRNA anticodon triplets and the number of tRNAGly isoacceptors. In the specifier loop column, the red underlined sequences indicate the potential SL sequence and the bold letters correspond to nucleotides of the SL codon-like triplets for glycine. H.aur: Herpetosiphon aurantiacus, D.geo: Deinococcus geothermalis, B.sub: Bacillus subtilis, B.cer: Bacillus cereus, C.tet: Clostridium tetani, C.bot: Clostridium botulinum, C.ace: Clostridium acetobutylicum, C.dif: Clostridium difficile, E.fae: Enterococcus faecalis, S.aur: Staphylococcus aureus, S.epi: Staphylococcus epidermidis, S.sap: Staphylococcus saprophyticus, S.san: Streptococcus sanguinis, S.mut: Streptococcus mutans, S.pne: Streptococcus pneumoniae, S.aga: Streptococcus agalactiae, L.inn: Listeria innocua, L.mon: Listeria monocytogenes.