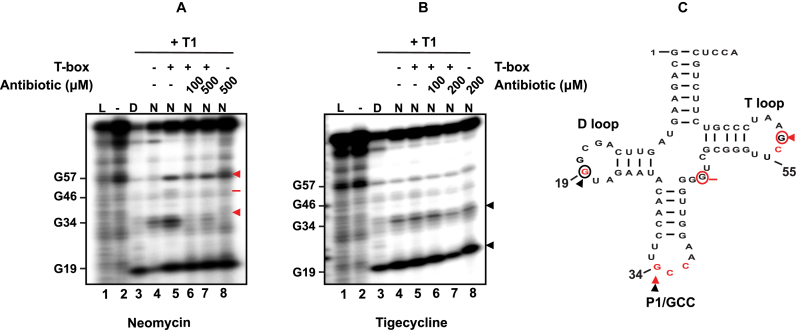
Figure 4.
Probing analysis of tRNAGlyGCC in the presence of neomycin B (A) or tigecycline (B). Enzymatic probing analysis of the tRNAGlyGCC (20 pmol) in the presence of the full-length S. aureus glyS T-box (60 pmol) and/or increasing concentrations of neomycin B or tigecycline. Red and black arrows indicate base protection from RNase T1 cleavage in the presence of neomycin B and tigecycline, respectively. Red bar shows a weak base protection in the presence of neomycin B. (D) indicates denaturing conditions, (N) native conditions and (L) alkaline hydrolysis ladder. (Bottom panel) The secondary structure of the S. aureus tRNAGlyGCC is shown (C); based on the available crystal structure, red nucleotides are important for interaction with the Stem I (25). Red circled nucleotides and red arrows show the binding sites of neomycin B and black circled nucleotides and black arrows the binding sites of tigecycline on the tRNAGlyGCC.