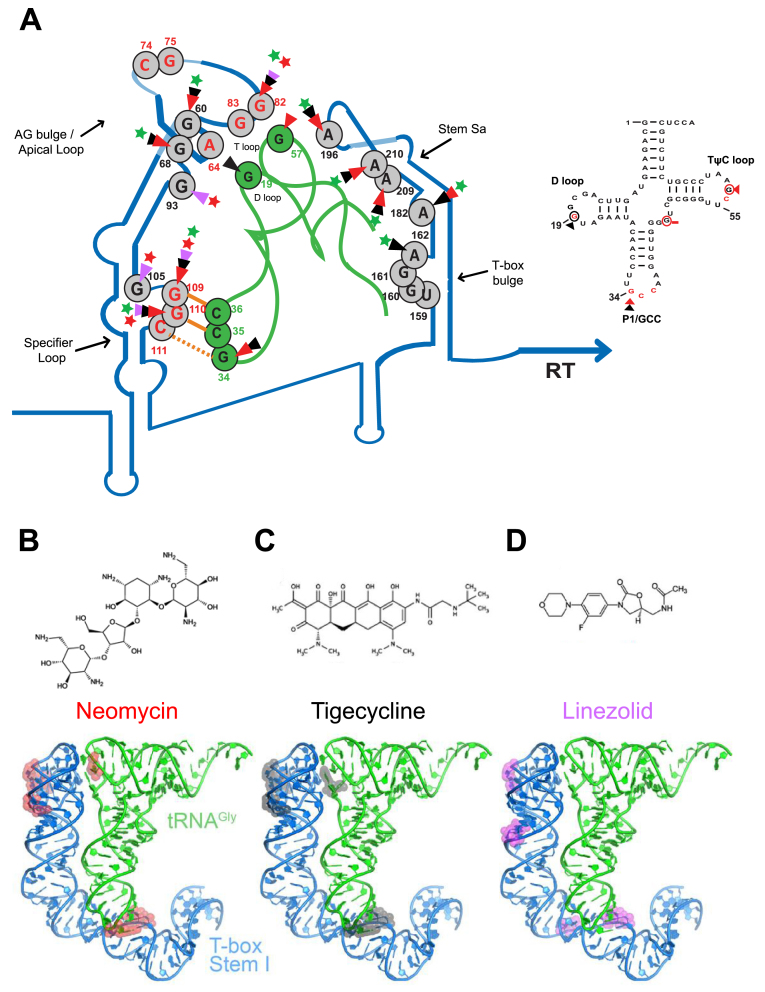
Figure 7.
Illustration of the proposed model of neomycin B, tigecycline and linezolid binding sites on the S. aureus glyS T-box:tRNAGlyGCC complex (A) and the secondary structure of the S. aureus tRNAGlyGCC. The protected bases on the S. aureus glyS T-box:tRNAGlyGCC in the presence of neomycin B (B), tigecycline (C) and linezolid (D) are indicated with different colored arrows; red arrows correspond to neomycin B interaction, black arrows to tigecycline and magenta arrows to linezolid. Green or red stars show the enhancement or blocking of the glyS T-box read-through transcription by the antibiotics tested, respectively. Orange lines show the GCC codon-anticodon like interaction and the orange dashed line the wobble pairing. Numbers indicate the position of each nucleotide on the S. aureus glyS T-box or the tRNAGlyGCC (in green). Red nucleotides at the apical loop show the bases that interact with the tRNA elbow based on the crystal structure (25) (Right panel); based on the available crystal structure, red nucleotides are important for interaction with the Stem I. Red circled nucleotides and red arrows correspond to the binding sites of neomycin B, and black circled nucleotides and black arrows show and tigecycline on the tRNAGlyGCC.