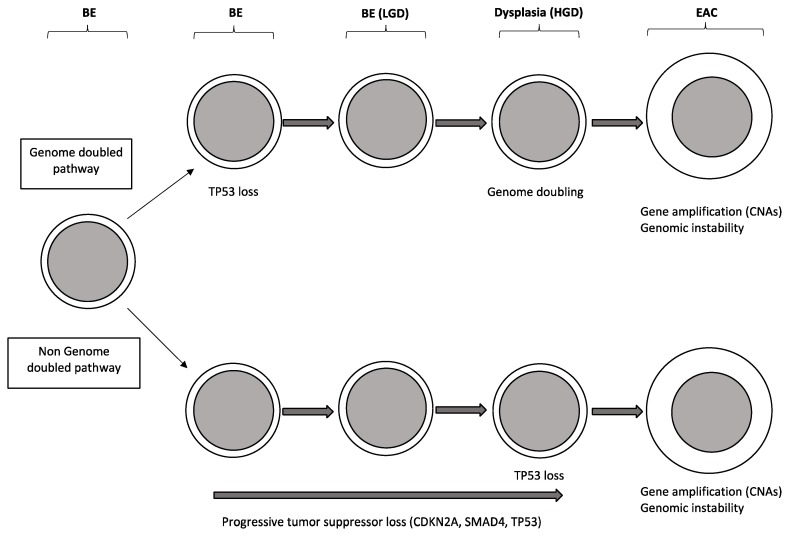
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of two possible pathways of BE progression to EAC. The top model shows the tumor progression pathway involving genome doubling: this pathway implies the early occurrence of TP53; the genome doubling leads to genomic instability, oncogene amplification with frequent copy number alterations and aneuploidy. The bottom model shows the BE progression to EAC involving the gradual and progressive accumulation of tumor suppressor losses, followed by activation of oncogenes and development of genomic instability. Abbreviations: CAN: copy number alteration; BE: Barrett’s esophagus; LGD: low-grade dysplasia; HGD: high-grade dysplasia. This model is based on data reported by Stachler et al. [27].