Fig. 1.
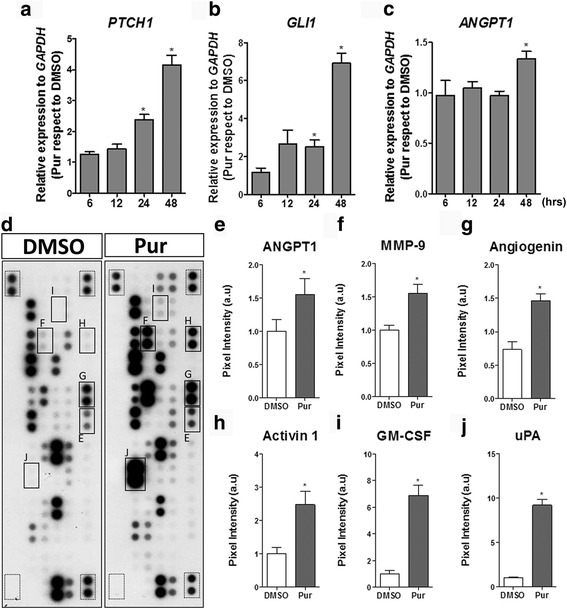
WJ-MSC are responsive to SHH pathway modulation increasing their angiogenic secretome. WJ-MSC were stimulated with purmorphamine (Pur) or DMSO (vehicle) in serum absence for the time points indicated, and transcript levels of (a) PTCH1, (b) GLI1, canonical SHH target genes, and (c) ANGPT1, a well described angiogenic factor, were determined by qPCR using GAPDH as a normalizing gene. The increment in gene expression is directly indicative of positive pathway signaling. *P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA for three independent umbilical cord samples. To determine the effect of SHH pathway activation in WJ-MSC, conditioned medium (CM) was obtained after 48 h of Pur stimulation and the presence of angiogenic factors was determined by Proteome Profiler Array. d Representative membranes showing CM from DMSO and Pur-stimulated WJ-MSC; squares indicate molecules in which quantifications are depicted (dotted squares indicate internal positive and negative controls). The SHH pathway regulates the secretion of (e) angiopoietin 1 (ANGPT1), (f) matrix metallopeptidase-9 (MMP-9), (g) angiogenin, (h) activin A, (i) granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and (j) urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). *P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test; CM were obtained from four different WJ-MSC samples
