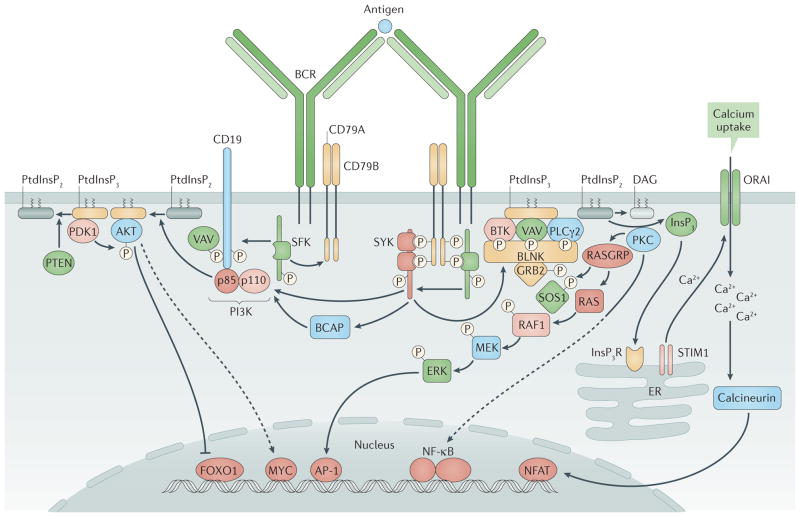
Figure 3. B cell receptor signalling.
In the assembled B cell receptor (BCR), CD79A–CD79B is weakly bound by Src family kinases (SFKs). Antigen binding promotes tyrosine phosphorylation of CD79A and CD79B on their immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs)9,169. Phosphorylated ITAMs recruit spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) and upregulate its kinase activity52,170. CD19 functions as a BCR co-receptor, leading to tyrosine phosphorylation within YXXM motifs in the cytoplasmic tail of CD19 that recruit the p85 regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)53,55,171 (left). PI3K activation mediated through this pathway or by the adaptor protein B cell adaptor for PI3K (BCAP)55 mediates phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PtdInsP2), generating phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdInsP3), which recruits AKT, 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1), Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) and other enzymes that are essential for signal propagation172. In a distinct pathway (right), B cell linker protein (BLNK)173 functions as a scaffold and substrate for SYK- and SFK-mediated phosphorylation, promoting the recruitment of phospholipase Cγ2 (PLCγ2), BTK, VAV guanine nucleotide exchange factor proteins174 and growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2). Activated PLCγ2 hydrolyses PtdInsP2 to diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3), which promotes Ca2+ mobilization through the InsP3 receptor (InsP3R) and opening of the plasma membrane Ca2+ channel ORAI. DAG recruits protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms and RAS guanyl-releasing proteins (RASGRPs). During positive selection of immature B cells, AKT activity suppresses forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) nuclear localization, which turns off recombination-activating gene (RAG) expression, and increases production of the transcription factor MYC, which (together with AKT) promotes cell survival. Another BCR-triggered pathway involves the guanine nucleotide exchange factor son of sevenless 1 (SOS1), the small GTPase RAS, the serine kinase RAF1, MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs). Ca2+ mobilization through InsP3R and ORAI promotes the activation of calcineurin and the nuclear localization of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT). PKC activation promotes activation of nuclear factor−κB (NF−κB). PI3K and its downstream activities seem to be promoted in immature B cells by the unligated BCR, whereas BCR ligation activates the BLNK pathway transiently. This leads to BCR internalization and reduced signalling through both pathways, and drives RAG expression, developmental arrest and cell starvation. AP-1, activator protein 1; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homologue; STIM1, stromal interaction molecule 1. Adapted with permission from REF. 175, F1000Research.