Figure 10. Schematic illustration of ER stress and autophagy flux after TBI.
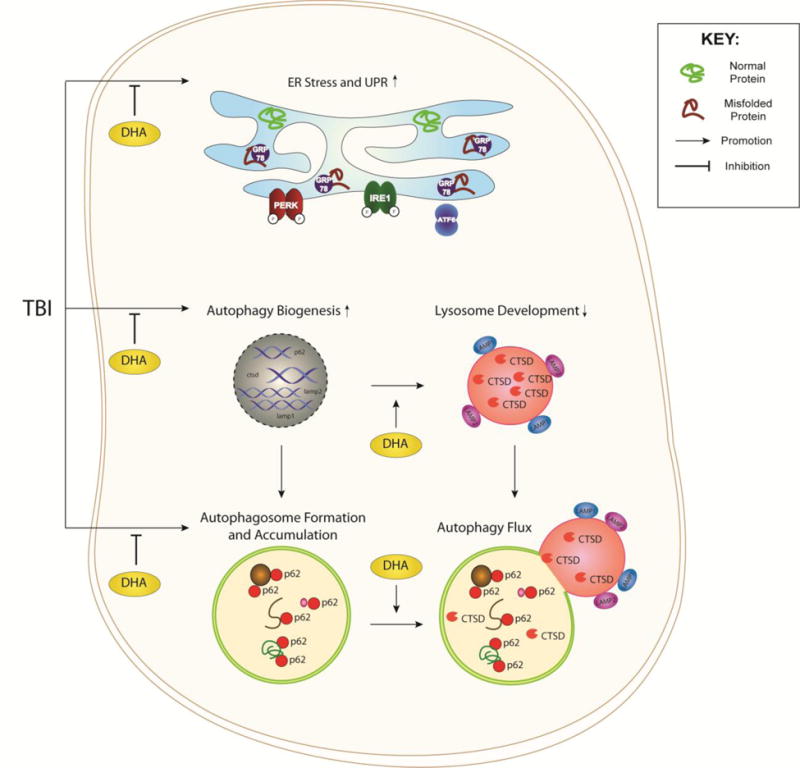
TBI induces ER stress through a surge of damaged and misfolded proteins within the ER. The UPR is triggered when the ER chaperone protein GRP78/BIP is dissociated from the ER-transmembrane sensors (PERK, IRE1, and ATF6) and bind to the misfolded proteins. TBI also stimulates autophagy biogenesis through the transcription of the related p62, ctsd, lamp1, and lamp2 genes and formation and accumulation of autophagosomes. UPR and autophagy stimulation actions are interconnected by the additional autophagic demand to recycle damaged protein and organelle detritus or when the efficiency of autophagy flux is compromised. In TBI brains, lysosomal development and function in neurons is diminished by a reduced mature CTSD expression or activity despite of its increased transcription. Autophagy flux is thus disrupted by the inefficiency in clearing cargo, leading to the observed accumulation of p62. DHA reduces ER stress, promotes CTSD efficiency and development of lysosomes and autophagy flux.
