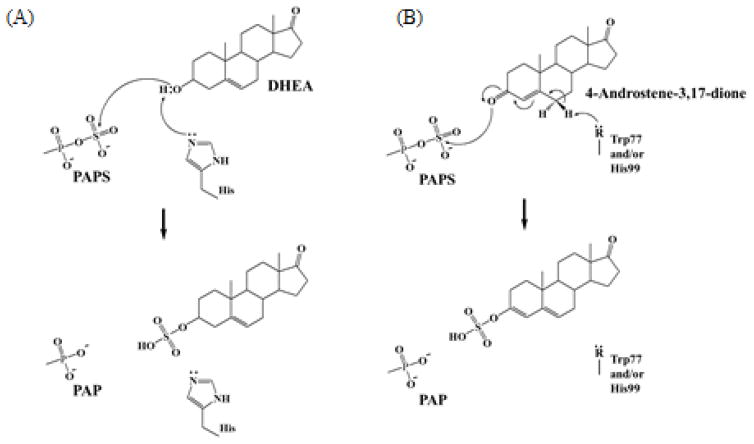
Figure 6. Proposed sulfation mechanism for steroids in the active site of hSULT2A1.
(A) Conventional enzymatic mechanism of SULT-mediated sulfation of DHEA [29]. (B) Proposed mechanism for the sulfation of ketosteroid by SULT2A1. In this model, the highly conserved His99 and W77 may collaboratively act to deprotonate the C-6 proton of 4-androstene-3,17-dione to form a enolate intermediate. The resulting nucleophilic oxyanion then attacks the sulfur of PAPS via a SN2 reaction, followed by the production and release of sulfated 4-androstene-3,17-dione from the active site.