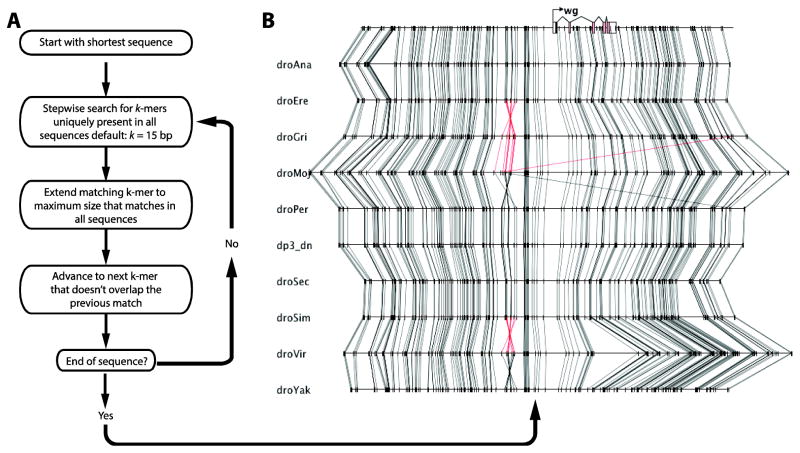
Figure 3. Sequence comparison function identifies identical k-mers that serve as anchor-points for alignment.
(A) Sequence alignment algorithm. Among the sequences to be aligned, the algorithm selects the shortest sequence to reduce calculation time. The algorithm determines whether each subsequence of specified length (default k = 15) is perfectly conserved and unique in each sequence, and advances to the next subsequence until the end of the shortest sequence is reached. (B) The output is displayed in the Graphical View.