Figure 1. Schematic view of the proposed viral etiology of prostate cancer.
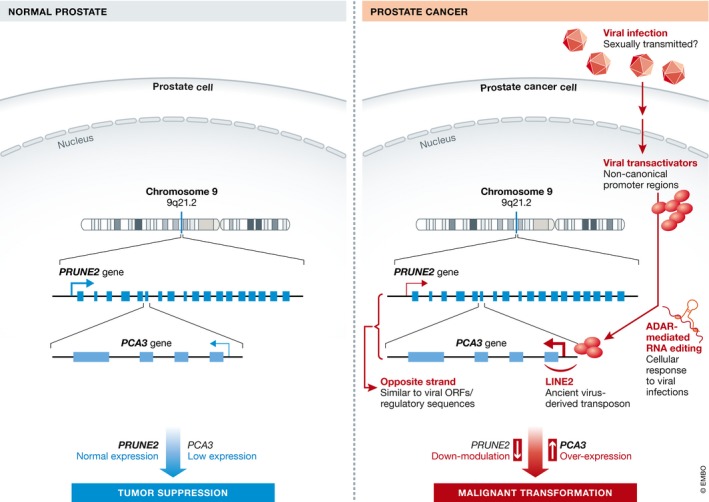
In the normal prostate, basal expression of PRUNE2 correlates with low PCA3 levels. In prostate cancer, a putative oncovirus could activate PCA3 expression through a direct transactivation of a cryptic, ancient virus‐derived promoter, resulting in downmodulation of PRUNE2, and leading to dysregulated cell proliferation and acquisition of malignant attributes.
