Figure 3.
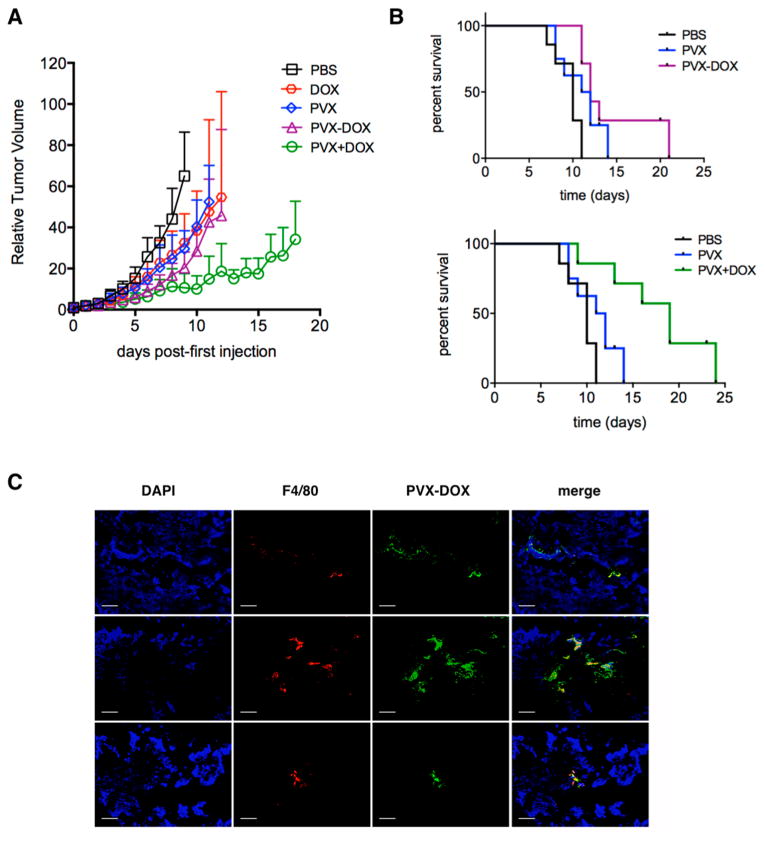
Chemo-immunotherapy treatment of B16F10 tumors. Groups (n = 6) were treated with PBS, PVX, DOX, PVX−DOX, or PVX+DOX. PVX was administered at a dose of 5 mg kg−1, DOX was administered at a dose of 0.065 mg kg−1. Treatment started ∼8 days post induction when tumors measured <100 mm3, and injections were repeated every other day until tumors reached >1000 mm3. (A) Tumor growth curves shown as relative tumor volume. Statistical significance was detected comparing PVX versus PVX+DOX. (B) Survival rates of treated mice. (C) Immunofluorescence imaging of three representative PVX−DOX tumor sections after weekly dosing of PVX−DOX (animals received two doses of PVX and were collected when tumors reached >1000 mm3). Tumors treated with PVX−DOX (rows 1–3) were sectioned and stained with DAPI (blue), F4/80 (red), and PVX (green). Scale bar = 100 μm.
