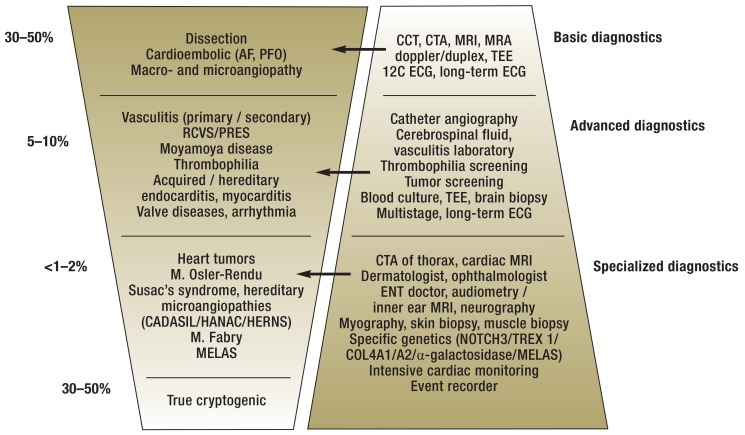
Figure 2.
Stage diagnostics and frequency distribution of stroke etiologies of young adult stroke
AF, artial fibrillation; CADASIL, cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (due to mutation in the NOTCH3 gene); CCT, cranial computed tomography; CTA, CT angiography; HANAC, hereditary angiopathy, nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps (due to COL4A1 / A2 gene mutations); HERNS, hereditary endotheliopathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, and stroke (due to TREX1 gene mutation); MELAS, mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes; MRA, magnetic resonance angiography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PFO, patent foramen ovale; PRES, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; RCVS, reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography; 12C ECG, 12-channel electrocardiogram