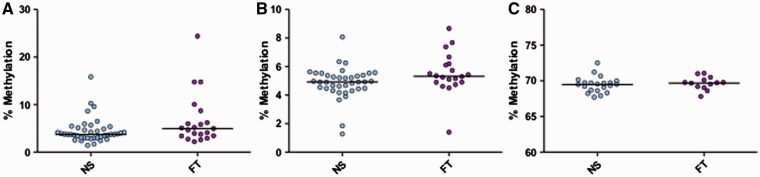
Figure 3.
Mitochondrial and global methylation associated with maternal smoking during pregnancy in foreskin. Median methylation % was measured for each pyrosequencing assay from foreskin of infants of the Kentucky birth cohort. Mitochondrial LDLR1 showed a trend of increased methylation in FT pregnancy smokers ( n = 21) vs. NS ( n = 41) ( P = 0.08, Mann–Whitney) (A). Mitochondrial HDLR1 showed significantly increased methylation in FT pregnancy smokers ( n = 20) vs. NS ( n = 38) ( P = 0.04, Mann–Whitney) (B) (four individual samples failed pyrosequencing assay for HDLR1). Horizontal lines represent the median. Global methylation measured via LINE-1 (C) showed no differences between the groups ( P = 0.58, t -test), (FT n = 13, NS n = 21). Horizontal lines represent the mean (LINE-1)