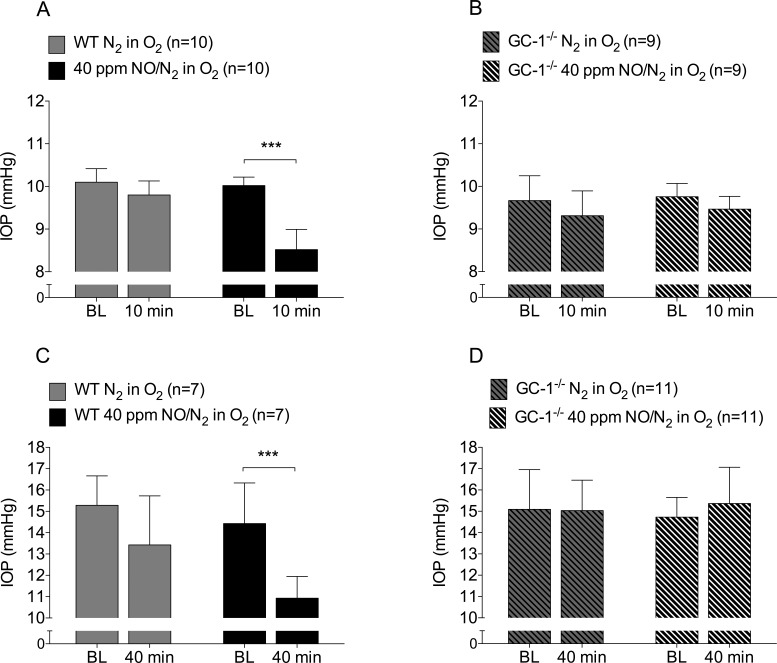
Figure 1.
Breathing NO gas lowers IOP in WT but not GC-1−/− mice. (A) Breathing 40 ppm NO (n = 10, ***P < 0.001), but not control gas (n = 10, P = 0.11), lowered IOP in anesthetized WT mice. (B) In contrast, breathing 40 ppm NO did not lower IOP in anesthetized GC-1−/− mice (n = 9, P = 0.08). (C–D) Breathing control gas did not affect IOP in awake WT (n = 7, P = 0.06) or GC-1−/− mice (n = 11, P = 0.93). Breathing 40 ppm NO for 40 minutes lowered IOP in awake WT mice (n = 7, ***P < 0.001) but not in awake GC-1−/− mice (n = 11, P = 0.20). BL, baseline.