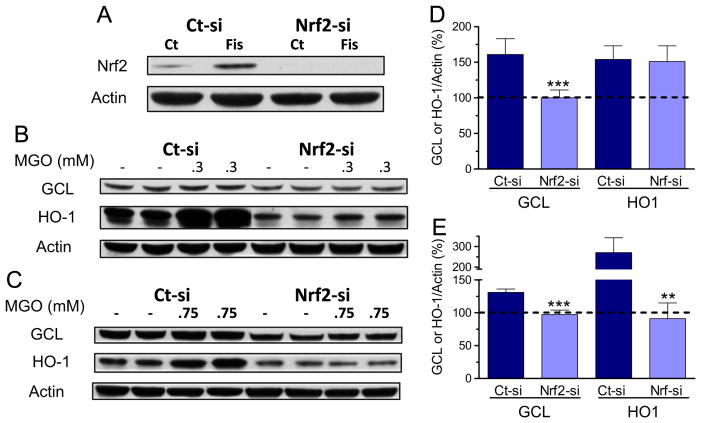
Fig. 7.
siRNA targeting of Nrf2 prevents the MGO-induced increase in GCL and HO1 expression in HT22 cells. (A) Cells were transfected with control (Ct-si) or Nrf2 siRNA (Nrf2-si), and further treated for 4 h with fisetin (10 μM), a known Nrf2 inducer. Nuclear extracts were prepared and blotted for Nrf2. Note that basal Nrf2 expression was decreased by its siRNA, and the strong fisetin-dependent induction of Nrf2 was abolished in cells treated with siRNA to Nrf2. After transfection with control-si or siRNA to Nrf2, cells were exposed to 0.3 mM MGO for 8 h (B and D), or 0.75 mM for 24 h (C and E). Cytosolic extracts were probed with GCL or HO-1 antibodies, shown as representative images (B and C) and their respective quantification (D and E). Densitometric data were normalized to actin content and expressed as percentage of untreated control. Data on graphs are presented as means ± SEM (N=3–5). P<0.01 (**) or 0.001 (***) indicate significant differences relative to their respective control siRNA (Ct-si).