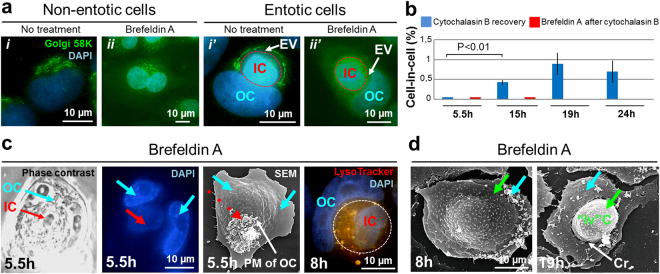
Figure 7.
Disassembly of the Golgi apparatus inhibits entosis in A431 cell monolayer. (a) Fluorescence micrographs of cells stained with anti-p58K antibodies and DAPI demonstrate localization of the Golgi apparatus in untreated (i, i’) and brefeldin A-treated (ii, ii’) non-entotic and entotic cells. i, Golgi is located near the nucleus; i’, redistribution of the Golgi apparatus during entosis: Golgi is localized around the entotic vacuole (EV) in outer cell (OC) (stage II). Panels ii, ii’ show disassembly of the Golgi apparatus in non-entotic and entotic cells after brefeldin A treatment. (b) Time-course changes in the frequency of entosis: blue column, 48 h incubation with cytochalasin B followed by a recovery for 5.5, 15, 19 and 24 h; red column, 48 h incubation with cytochalasin B followed by a recovery for 15 min and treatment with brefeldin A for 5.5, 15, 19 and 24 h. Note a gradual increase in cell-in-cell structures after cytochalasin B recovery whereas an additional brefeldin A treatment caused a complete inhibition of entosis. Results are shown as means ± SD. n = 1,000 cells were counted per each of three independent experiments. (c) Correlative light and electron microscopy of cell-in-cell structure 5.5 h after brefeldin A treatment. Shown are representative phase-contrast micrograph, DAPI staining, and scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of the same cell-in-cell structure. The inner cell (IC) is covered by the plasma membrane of OC. Red arrow, IC; blue arrows, two nuclei of the entotic cell; dashed red arrow, protuberances of OC plasma membrane. Right panel shows the pattern of lysosome staining with LysoTracker (orange) of IC and OC 8 h after brefeldin A treatment. PM of OC, plasma membrane of outer cell. (d) Scanning electron micrographs of cells 8 h (left) and 19 h (right) after brefeldin A treatment. Green arrows point to the cell spreading over the apical surface of the substrate-attached cell (left) and to the round-shaped cell located at the crater-like (Cr) deformation of the substrate-attached cell plasma membrane (right). Note, that the plasma membrane of substrate-attached cell doesn’t cover such “invading” cell (“Iv”C). Blue arrows, substrate-attached cells.