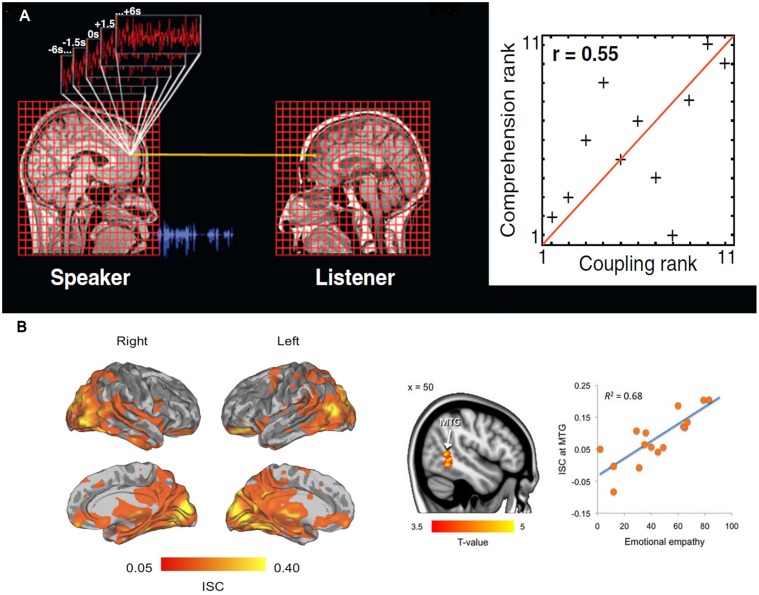
FIGURE 3.
(A) Inter-subject correlation (ISC) between hemodynamic responses of a speaker listener pair during storytelling. The neural coupling was assessed through the use of a general linear model in which the time series in the speaker’s brain are used to predict the activity in the listeners’ brains. The second part of the figure shows that, the greater the neural coupling between a speaker and listener the better the understanding. Adapted from “Speaker-listener neural coupling underlies successful communication,” by Stephens et al. (2010). (B) Inter-subject correlation while watching movies depicting unpleasant, neutral, and pleasant emotions. Brain regions showing statistically significant [P < 0.05, false discovery rate (FDR) corrected] group-level ISCs during viewing of film clips. Tendency to catch others’ emotions as indexed by Measure of Emotional Empathy in individual subjects was associated with ISC in the right middle temporal gyrus (P < 0.05, FDR corrected). ISC scores in the right panel are averages from an 8-mm sphere drawn around the peak voxel. Adapted from “Emotions promote social interaction by synchronizing brain activity across individuals,” by Nummenmaa et al. (2012).