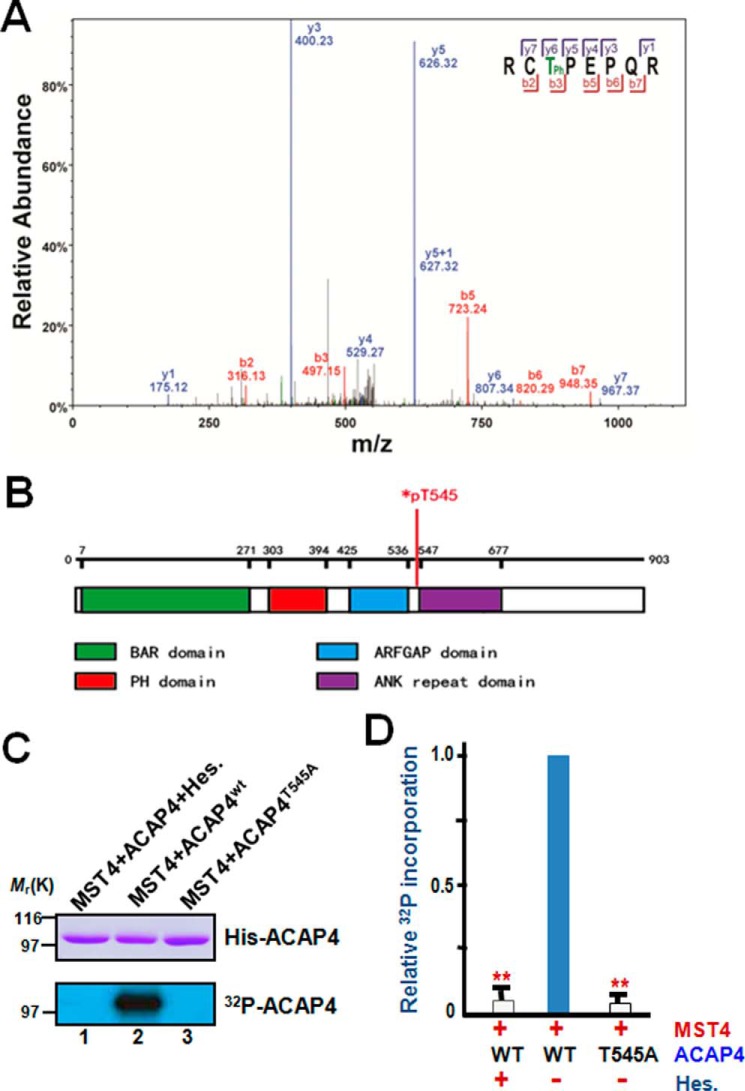
Figure 2.
ACAP4 is a novel substrate of MST4 and is phosphorylated during parietal cell secretion. A, representative phosphopeptide mass spectrum from ACAP4 isolated from secreting parietal cells. A representative band from SDS-PAGE shown in Fig. 1A (lane 1) was removed for trypsin digestion followed by mass spectrometric analyses as detailed under “Experimental procedures.” The annotated spectra from mass spectrometric analyses indicate that ACAP4 is phosphorylated at Thr545 in secreting parietal cells. B, schematic illustrating the functional domains of ACAP4 and annotating the location of pThr545. C, Thr545 of ACAP4 is a substrate of MST4 in vitro. Aliquots of recombinant His6-tagged ACAP4 were purified and incubated with MST4 or MST4 plus its chemical inhibitor hesperadin (Hes.) as detailed under “Experimental procedures.” As a control, we used an aliquot of recombinant ACAP4 with the putative MST4 site mutated to alanine (ACAP4T545A, lane 3). Top panel, Coomassie Blue–stained SDS-PAGE. Bottom panel, 32P incorporation from the same gel. D, quantitative analyses of in vitro phosphorylation efficiency in C. **, p < 0.01 compared with wild-type ACAP4 controls. Error bars represent the standard error of three separate preparations.