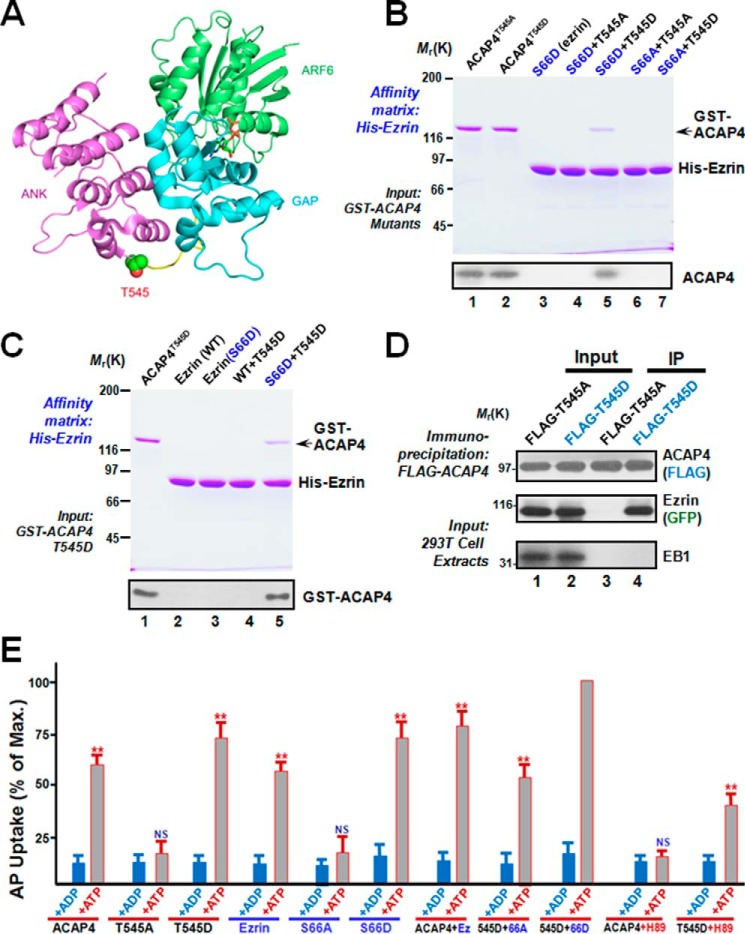
Figure 4.
Phosphorylation of Thr545 is essential for ACAP4–ezrin interaction and parietal cell acid secretion. A, a canonical ARF–ARFGAP complex (PDB code 3LVQ) structure shown as a schematic with ARF6 in green, the GAP domain in cyan, and the ANK repeat in purple. The linker between the ACAP4 GAP domain and ankyrin repeat is colored in yellow. The Thr545 side chain important for phosphorylation is represented as spheres. The figure was generated by PyMOL software (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 1.8 Schrödinger, LLC). B, phosphorylation of ACAP4 at Thr545 specifies its association with ezrin. Various His6–ezrin proteins were purified on nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid beads, followed by incubation with GST-ACAP4T545D and GST-ACAP4T545A proteins. Beads were washed and boiled in SDS-PAGE sample buffer, followed by SDS-PAGE analyses of proteins bound to the beads. Western blotting analyses, shown in the bottom panel, confirmed that ACAP4T545D selectively binds to EzrinS66D. C, phosphorylation of Thr545 of ACAP4 specifies its association with phospho-mimicking ezrinS66D. Both wild-type and phospho-mimicking ezrinS66D proteins were purified on nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid beads, followed by incubation with GST-ACAP4T545D protein. Beads were washed and boiled in SDS-PAGE sample buffer, followed by SDS-PAGE analyses of proteins bound to the beads. Western blotting analysis, shown in the bottom panel, confirmed that ACAP4 T545D selectively binds to ezrinS66D but not wild-type ezrin. D, phosphorylation of Thr545 of ACAP4 specifies its association with ezrin in 293T cells. An immunoprecipitation (IP) assay was used to demonstrate the complex formed by ACAP4T545D and ezrin in cultured cells. Note that ACAP4T545A failed to form a complex with ezrin. E, phosphorylation of Ser66 on ezrin and Thr545 on ACAP4 synergize for parietal cell secretion. Gastric glands were SLO-permeabilized and incubated with various recombinant ezrin mutants mimicking Ser66 phosphorylation independently or as combination with ACAP4 mutants mimicking Thr545 phosphorylation before being stimulated with 100 μm cAMP plus 100 μm ATP, and AP uptake was measured as described under “Experimental procedures.” AP uptake was plotted as a percentage of the stimulated control for each experiment. Error bars represent S.E.; n = 5. *, significant difference from stimulated controls (**, p < 0.01); NS, no significant difference. Note that ezrin mutant mimicking Ser66 phosphorylation combined with ACAP4 mutant mimicking Thr545 phosphorylation exhibited greatest secretory activity in response to cAMP stimulation. cAMP-elicited ACAP4-dependent parietal cell secretion is inhibited by the PKA inhibitor H89.