Fig. 2.
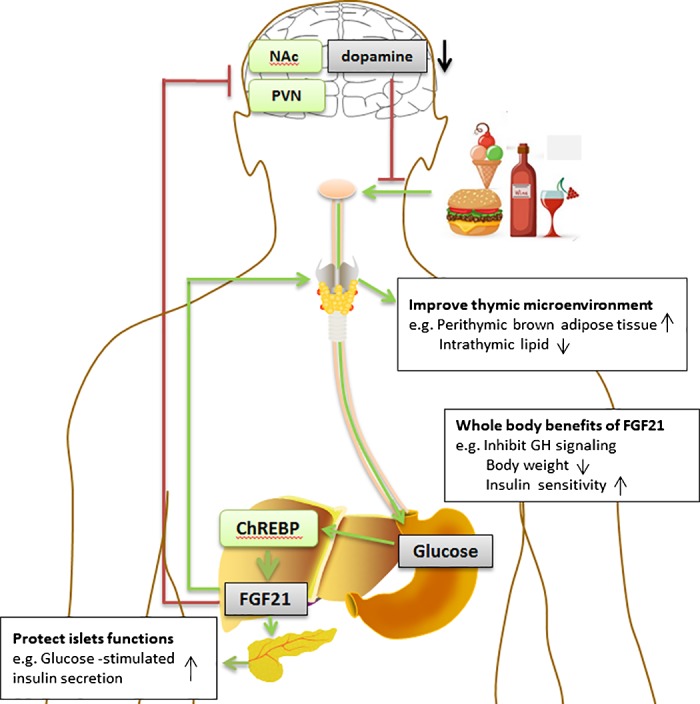
Role of FGF21 in metabolism and food preference. Dietary intake of carbohydrates activates ChREBP in the liver, which leads to the increased expression of FGF21 and its release into circulation. In the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), FGF21 acts as an endocrine factor to inhibit the consumption of carbohydrates and reduce levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), forming a potential negative feedback loop and restricting the reward derived from intake of sugars. Meanwhile, FGF21 shows beneficial immunoregulatory effects and regulates peripheral T cell homeostasis by preventing age-related thymic involution. From a whole body viewpoint, FGF21 inhibits GH signaling and reduces body weight to improve longevity and health status.
