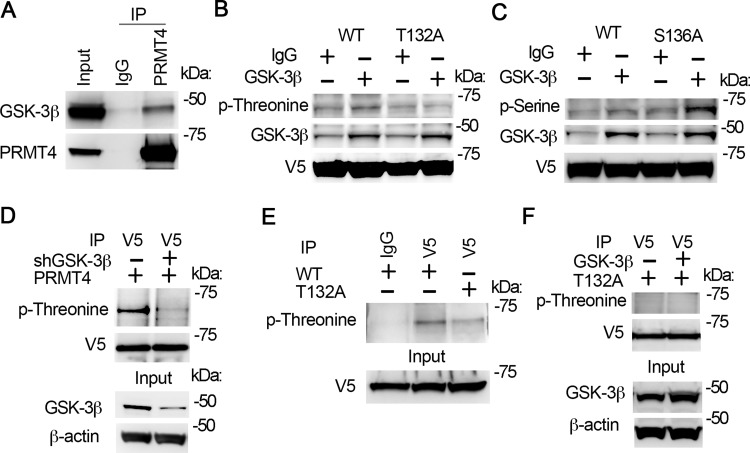
Fig. 3.
GSK-3β interacts with PRMT4 and catalyzes PRMT4 phosphorylation at T132. A: cell lysates were applied with PRMT4 immunoprecipitation (IP) study. PRMT4 precipitates were analyzed with GSK-3β and PRMT4 antibodies subsequently. B and C: GSK-3β in vitro phosphorylation of PRMT4 at T132. Wild-type (WT), T132A, and S136A PRMT4 mutant recombinants were synthesized with TnT expression system and in vitro phosphorylation assay was conducted with enzymatic active GSK-3β. Samples were analyzed with phospho-threonine antibody (B) or phospho-serine antibody (C). The GSK-3β signal in IgG lanes in B and C may be from TnT in vitro protein synthetic system. D: PRMT4 was expressed in GSK-3β-silenced cells. V5 immunoprecipitates were analyzed with phosphor-threonine and V5 immunoblotting. The inputs were analyzed with GSK-3β and β-actin immunoblotting. E: WT and T132A mutant PRMT4 were expressed in MLE12 cells, respectively. V5 immunoprecipitates were analyzed with phospho-threonine. Inputs were analyzed with V5 immunoblotting. F: T132A mutant PRMT4 was coexpressed with GSK-3β in MLE12 cells for 48 h. V5 immunoprecipitates were analyzed with phospho-threonine and V5 immunoblotting, respectively. The inputs were analyzed with GSK-3β and β-actin immunoblotting. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.