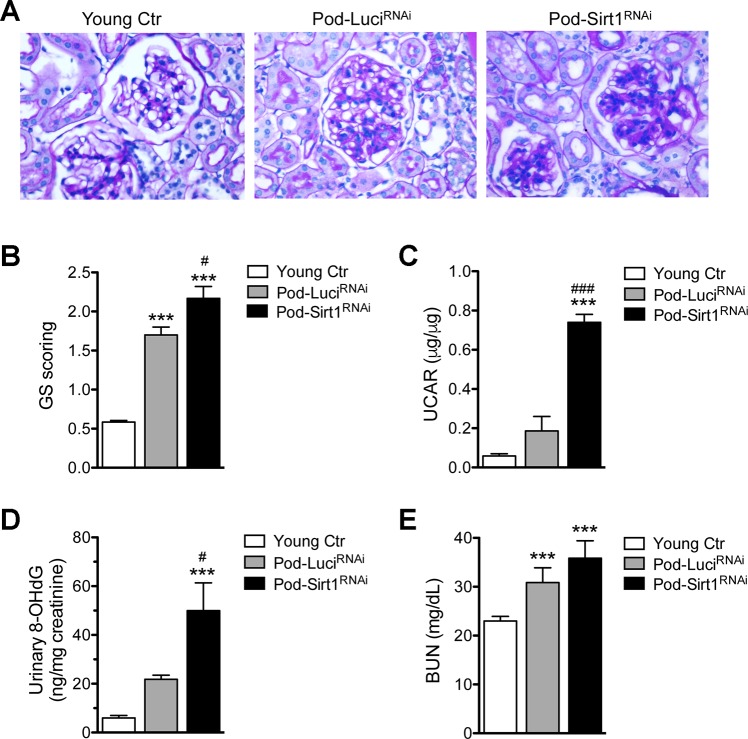
Fig. 2.
Podocyte-specific knockdown of Sirt1 exacerbates aging-related glomerulosclerosis and albuminuria. A: representative images of periodic acid-Schiff-stained kidney sections show increased glomerulosclerosis in aged Pod-Sirt1RNAi in comparison with Pod-LuciRNAi mice. B: semiquantitative scoring of severity of glomerulosclerosis (GS) in kidneys of mice in all groups. 50 glomeruli were counted per mouse. C: urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) is significantly increased in aged Pod-Sirt1RNAi mice compared with other groups. D: urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) normalized to creatinine is also significantly increased in aged Pod-Sirt1RNAi mice compared with other groups. E: renal function assessed by blood-urea nitrogen (BUN) is significantly increased in aged mice compared with young controls. ***P < 0.001, compared with young controls; #P < 0.05 and ###P < 0.001, compared with Pod-LuciRNAi mice (n = 6 mice in each group).