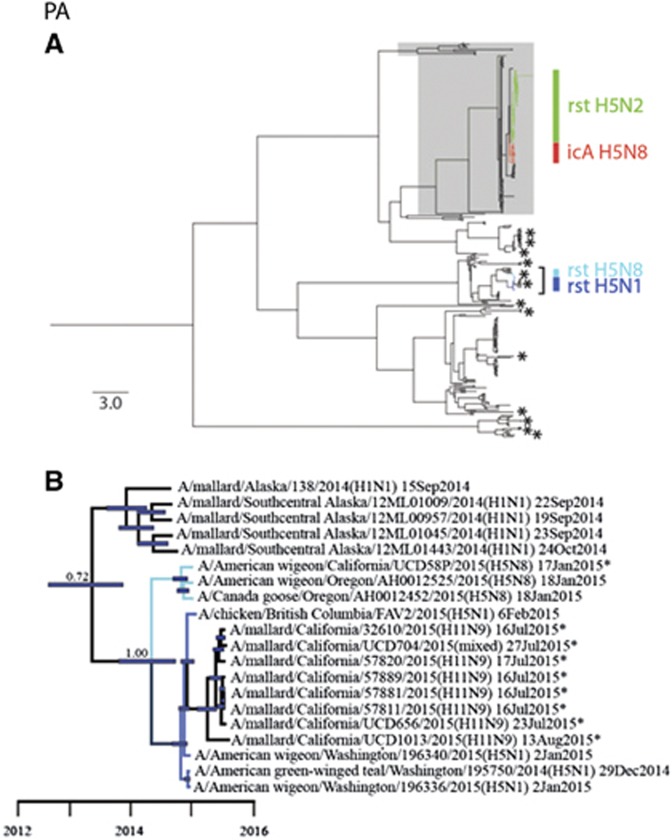
Figure 3.
Bayesian phylogenetic trees depicting the inferred genetic relationship among PA gene segment sequences for isolates originating from wild waterfowl in California from 2014–2015, highly pathogenic (HP) clade 2.3.4.4 H5 influenza A viruses detected in North America during the concurrent outbreak and other reference sequences for wild bird low-pathogenic (LP) influenza A viruses isolated from North America and East Asia. (A) The complete Bayesian phylogeny. Eurasian viral lineages are highlighted in gray. The approximate location of sequences for influenza A virus isolates from wild waterfowl that were sampled in California during the period from 2014 to 2015 are depicted with asterisks. Asterisks represent more than one closely related sequence in some instances. Branch tips for clade 2.3.4.4 HP H5 influenza A viruses detected in North America are color-coded and identified as follows: red=intercontinental lineage A HP H5N8 that was first introduced into North America; light blue=reassortant HP H5N8; dark blue=reassortant HP H5N1; and green=reassortant HP H5N2. The bracket indicates the portion of the phylogeny that is presented in panel B. Inferred evolutionary distance is indicated by the scale bar. (B) partial PA phylogeny to depict inferred genetic ancestry among strain A/American wigeon/California/UCD58P/2015(H5N8), other reassortant HP H5N1 and H5N8 viruses detected in North America and other LP influenza A viruses that were isolated in California as part of this study or elsewhere as part of concurrent surveillance efforts. Color is used to differentiate among branch tips for HP reassortant H5N1 (dark blue), HP reassortant H5N8 (light blue) and LP influenza A viruses (black). Asterisks are used to indicate genetic sequences produced as part of the current study. Blue bars at nodes depict 95% highest posterior densities, which can be interpreted relative to the provided timescale. The posterior probability of a node that depicts inferred common ancestry between reassortant HP H5N1 and HP H5N8 influenza A viruses with LP viruses detected in mallards sampled in California as part of this study is shown. Refer to Supplementary Figure S3 for the complete phylogenetic tree with tip labels.