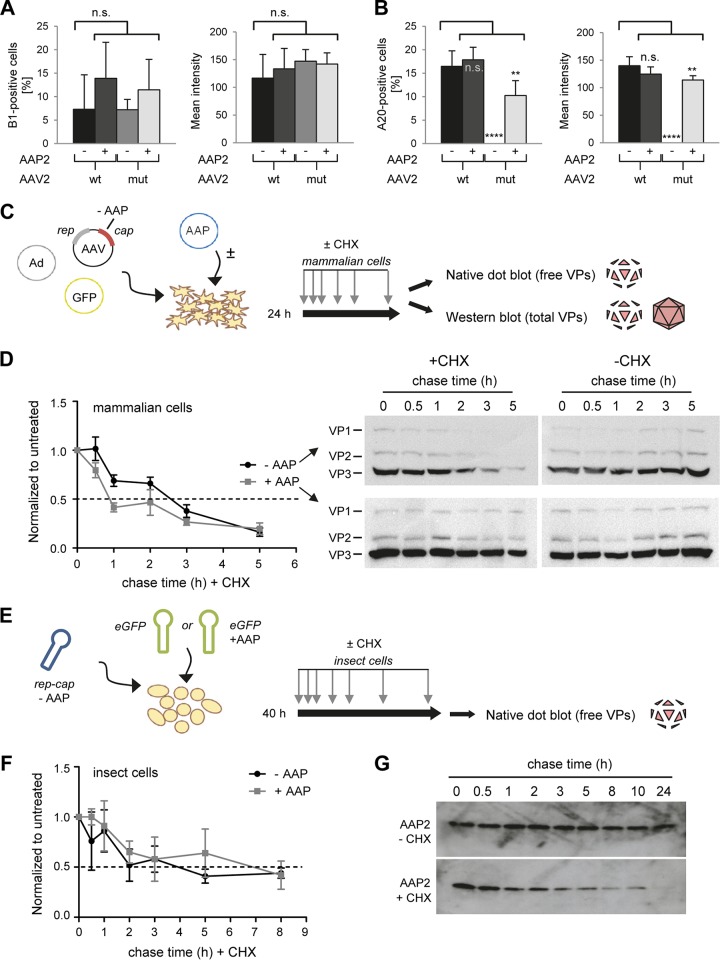
FIG 3.
Determination of the half-lives of AAV2 VP proteins and of AAP2. (A and B) Quantification of AAV2 VP proteins (A) or assembled particles (B) in microscopy pictures (not shown) of cells stained with the B1 or A20 antibody at 48 h posttransfection. Six pictures per condition were analyzed with the CellProfiler program to determine percentages of positive cells or mean integrated intensities of stained cells. **, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant. (C and D) Determination of the VP protein half-life in mammalian cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with the AAV2mut helper plasmid with or without the AAP2 expression plasmid. Cycloheximide (CHX) treatment was started at 24 h after transfection, and samples were collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 5 h after CHX treatment. Part of the sample was processed for Western blot analysis, while the remainder underwent freeze-thaw cycles for nondenaturing dot blot analysis. Dot blots were hybridized with the B1 antibody to detect unassembled, free VP proteins. The signal of each dot was quantified with Image J software and normalized to the untreated (no CHX) condition at each time point. A technical duplicate was performed and analyzed for each biological replicate (n = 3). Plotted on the left in panel D are the means with the standard errors of the mean (SEM). The dashed line indicates a 50% signal reduction. Shown on the right in panel D are representative Western blots stained for total VP proteins (free and assembled) with the B1 antibody. (E and F) Determination of the VP protein half-life in insect cells. Sf9 cells were infected with AAP2-depleted BEV-Rep2Cap2 and BEV-eGFP or BEV-eGFP-Puro-p10AAP2 (encoding AAP2) at an MOI of 0.05 per baculovirus. CHX chase started at 40 h after BEV infection, and samples were collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5, and 8 h later. Native dot blotting and signal quantification were performed as described for HEK293T in panels C and D. The graph in panel F shows the means for three biological replicates with SD for each time point after normalization to the untreated condition (without CHX) and to t = 0 h. (G) Determination of the AAP2 half-life in insect cells. Sf9 cells were infected with BEV-Rep2Cap2 and BEV-eGFP at an MOI of 0.05 per baculovirus. CHX chase started at 40 h after BEV infection, and samples were collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 10, and 24 h later. The representative Western blots (from 10 μg of total proteins extracted from cell pellets at each time point) illustrate the rapid decline of AAP2 steady-state levels in the presence of CHX.