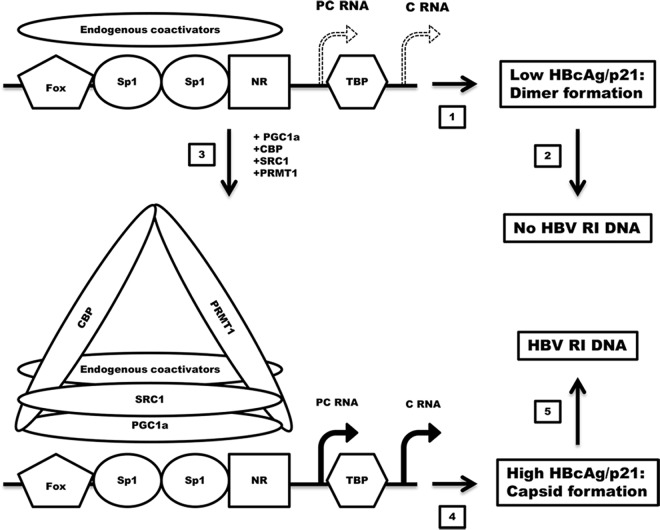
FIG 5.
Diagrammatic representation of the coactivators assembled on the HBV nucleocapsid promoter and their effects on HBV transcription, HBcAg/p21, HBcAg/capsid, and capsid-associated HBV replication intermediate (RI) DNA. PC RNA, HBV precore 3.5-kb RNA; C RNA, HBV pregenomic or core 3.5-kb RNA; Fox, fork head box transcription factor (56); Sp1, specificity protein 1 transcription factor (57); NR, nuclear receptor transcription factor (i.e., HNF4, RXR, PPAR, FXR, LRH1, and estrogen-related receptor [ERR]) (3, 6, 48); TBP, TATA-binding protein. (1 and 2) Endogenous coactivators support limited HBV 3.5-kb RNA expression (1) and relatively low levels of HBcAg/p21 polypeptide synthesis (2), which are not sufficient to support capsid formation, and hence, there is no viral DNA replication. (3) Recruitment of CBP, SRC1, and PRMT1 plus potentially additional endogenous coactivators by PGC1α to the HBV nucleocapsid promoter. (4) PGC1α, CBP, SRC1, and PRMT1 plus endogenous coactivators support modestly increased levels of HBV 3.5-kb RNA expression. (5) The translation of modestly increased levels of HBcAg/p21 polypeptide synthesis crosses a critical threshold that is required to support capsid formation and associated HBV DNA replication.