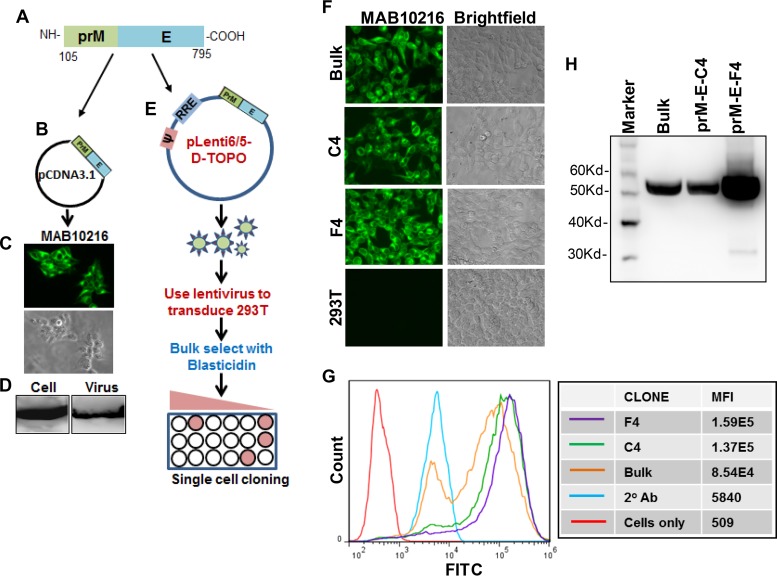
FIG 4.
Generation of prM-E cell line for VLP production. ZIKV prM-E was PCR amplified by use of specific primers, using the codon-optimized C-prM-E construct as the template (A), and cloned into the pCDNA3.1 expression vector (B). (C) E protein expression was determined by fluorescence microscopy after staining with the MAB10216 antibody. (D) Culture supernatants were harvested from ZIKV prM-E-expressing cells and ultracentrifuged. Cell and virus pellets were lysed, and E protein expression was determined by Western blotting. (E) ZIKV prM-E was PCR amplified and cloned into the lentiviral vector pLenti6/5-D-Topo. 293T cells were then transfected with the pLenti-prM-E construct along with the helper plasmid and VSV-G envelope, and ZIKV prM-E lentiviral particles were harvested at 48 h posttransfection. 293T cells were then transduced with the lentiviral particles, and cells were either bulk selected or selected as single-cell clones by culture in the presence of blasticidin. Selected cells were confirmed to have E protein expression via immunofluorescence assay after staining with the MAB10216 antibody (F) and by flow cytometry (G). The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of E protein expression for each prM-E clone is indicated on the right. (H) The indicated pLenti-ZIKV-prM-E cell clones were seeded in equal cell numbers, and culture supernatants were harvested and ultracentrifuged. VLP pellets were lysed and resolved by SDS-PAGE, and E protein expression was determined by Western blotting.