Fig. 1.
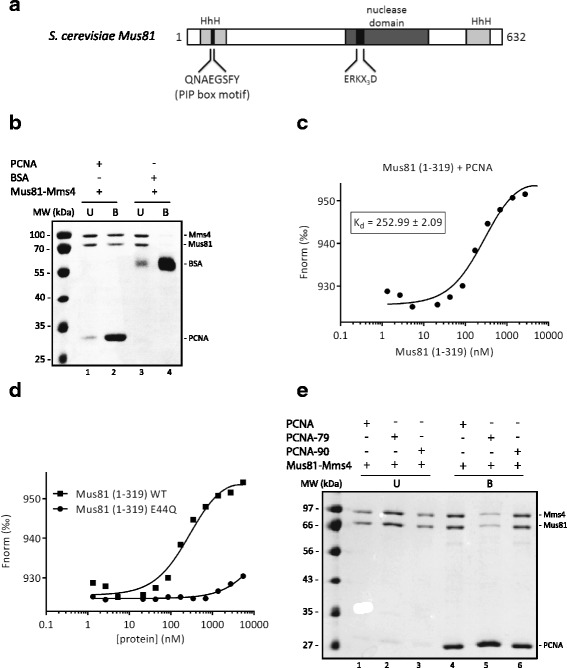
Interaction of the Mus81-Mms4 complex with PCNA. a Schematic representation of Mus81 protein with marked PIP box motif. b Purified recombinant Mus81-Mms4 (5 μg) was mixed either with PCNA or BSA covalently bound to Affi-beads in Tris buffer containing 100 mM KCl. After 30 min incubation at 4 °C the supernatant was removed and the beads were washed twice with Tris buffer containing 150 mM KCl. The unbound (U) and bound (B) fractions were then analyzed on 12% SDS gel. c Microscale thermophoresis measurement of interaction between PCNA and Mus81 (1–319). Fluorescently labeled PCNA (22 nM) was mixed with increasing concentrations (1.3–5500 nM) of Mus81 (1–319). The binding affinity of PCNA towards Mus81 (1–319) was quantified by MO.Affinity Analysis software. d Microscale thermophoresis measurement of the interaction between PCNA and Mus81 (1–319) wild-type and PIP-box mutant. Fluorescently labeled PCNA (22 nM) was mixed with increasing concentrations (1.3–5500 nM) of Mus81 (1–319) wild-type or E44Q mutant. The binding affinity of PCNA towards Mus81 variants was quantified by MO.Affinity Analysis software. e Purified recombinant Mus81-Mms4 (2.5 μg) was mixed with PCNA, PCNA-79, or PCNA-90 covalently bound to Affi-beads in Tris buffer containing 150 mM KCl. After 30 min incubation at 11 °C, the supernatant was removed and the beads were washed twice with Tris buffer containing 150 mM KCl. The reactions were analyzed as shown in b
