Fig. 7.
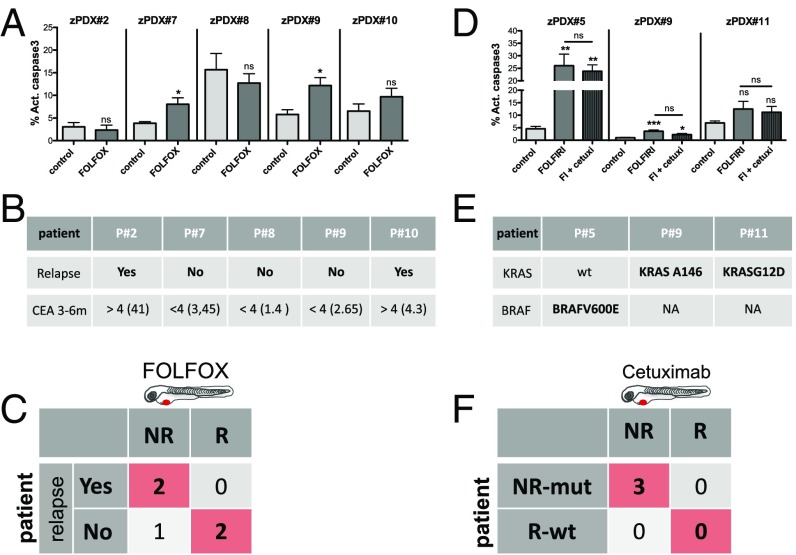
The zPDX treatment response may predict relapse and correlate with known genomic biomarkers of Cetuximab resistance. Five zPDX, corresponding to patients subjected to curative surgery and postoperative FOLFOX adjuvant treatment, were treated with FOLFOX for 3 days and processed for immunofluorescence. Cell death by apoptosis (A) (activated caspase3) was analyzed and quantified. The zPDX#7 control vs. FOLFOX P = 0.037; zPDX#9 control vs. FOLFOX P = 0.016. (B) Relapse and CEA levels information for the five patients analyzed. (C) Confusion matrix displays the number of patients with actual and predicted responses in zPDX, i.e., responders are patients that did not relapse (R), and patients that relapse are the nonresponders (NR). (D) Three zPDX were treated with FOLFIRI and with FOLFIRI in combination with Cetuximab, and cell death by apoptosis (activated caspase3) was analyzed. The zPDX#5 control vs. FOLFIRI P = 0.0043, and control vs. FOLFIRI+Cetuximab P = 0.0084; zPDX#9 control vs. FOLFIRI P = 0.001, and control vs. FOLFIRI+Cetuximab P = 0.012. (E) Genomic information of the analyzed patients. (F) Confusion matrix displays the number of patients with mutations predicted of resistance with predicted responses in zPDX. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant.