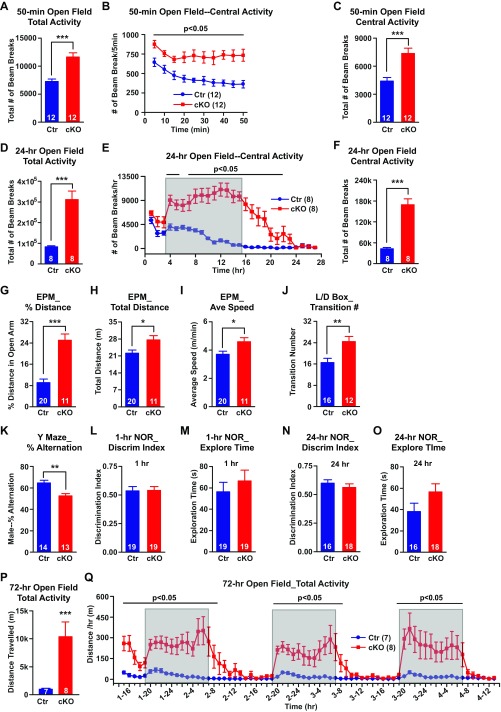
Fig. S4.
Behavioral characterization and drug rescue. (A–F) Increased locomotor activity of Ank-G cKO mice in the 50-min and 24-h open field test. (A and D) Sum of total activity in 50-min (A) and 24-h (D) tests. (B and E) Time point of central activity in 50 min (every 5 min, B) or 24-h (every hour, E). Shaded area in E indicates the typical active time of control mice. (C and F) Sum of central activity in 50-min (B) and 24-h (E) tests. (G–I) In the elevated plus maze (EPM) test, the percent distance Ank-G mice traveled in the open arm was much greater than control mice (G). Ank-G cKO mice traveled longer distance (H) and at faster speed (I) than control mice. (J) In a 6-min light/dark box test (L/D box), cKO mice had greater number of transitions between light and dark compartments than control mice. (K–O) Cognitive test of cKO mice. In Y maze test, cKO mice showed reduced percent of accurate alternations over total number of alternations among the three arms (K). (L–O) Novel object recognition test (NOR). cKO mice displayed similar discrimination index (the percent of time mouse explore novel object over the total time mouse explore old and novel objects) to control in 1-h (L) or 24-h (N) test. cKO mice spent similar time exploring both objects to control mice in 1-h (M) and 24-h (O) tests. (P and Q) Increased locomotor activity of Ank-G cKO mice in 3-d (72 h) open field test. (P) Total distance (in meters) traveled in 3 d. (Q) Distance (in meters) traveled every hour. Shaded areas in Q indicate the typical active time of control mice (7 AM–7 AM). A, C, D, and F–O and P used t test. B, E, and Q used two-way repeated measurement of ANOVA followed by post hoc t test. Bar graphs indicate mean ± SEM; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. The number of animals used in each group is indicated in parentheses.