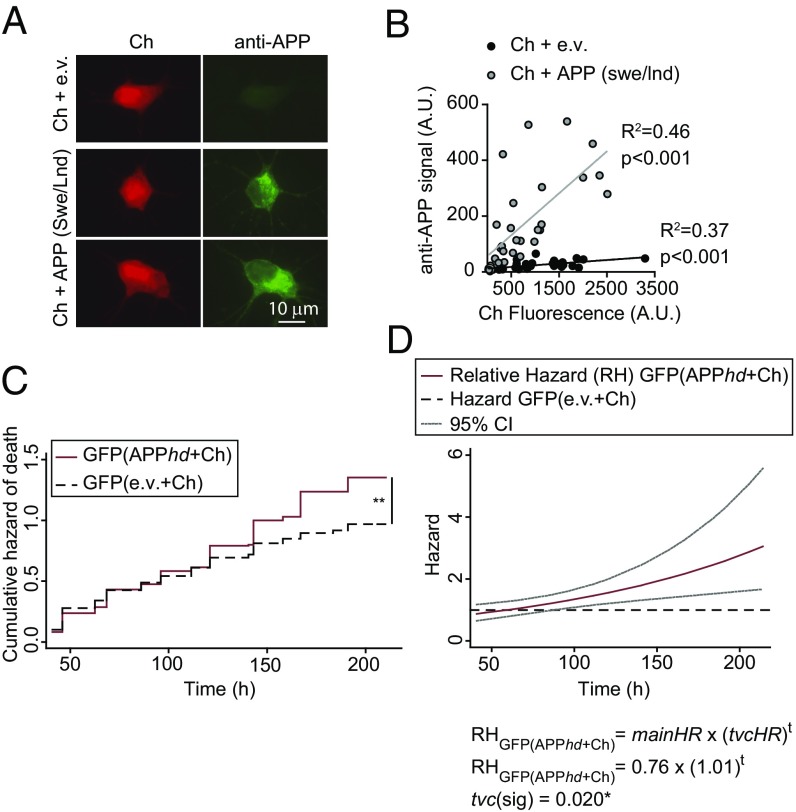
Fig. 7.
Neurons expressing APPswe/Lnd increase the risk of death of neighboring control neurons. (A) Primary rat cortical neurons were cotransfected with plasmids expressing APPswe/lnd or the empty vector (e.v.) and Ch and were immunostained with an APP-specific antibody. (B) Fluorescence intensity from Ch and from secondary antibodies recognizing APP was quantified in individual neurons. A correlation analysis was performed showing that Ch+ neurons expressed the APPswe/lnd protein compared with control conditions (e.v.). (C) Cumulative risk estimates of GFP-expressing neurons neighboring APP-expressing neurons transfected with a high dose of APP+Ch (APPhd+Ch) or control neurons (e.v.+Ch). CPH analysis of 250–300 neurons from two independent experiments: **P < 0.01. (D) Cox modeling of the time-dependent variation in the relative hazard in a population of neighboring APP-expressing neurons [GFP(APPhd+Ch)] with respect to a population of neighboring control neurons [GFP(e.v.+Ch)]. The main relative hazards at t = 0 and tvc are from Table S2 95% CIs.