Fig. S3.
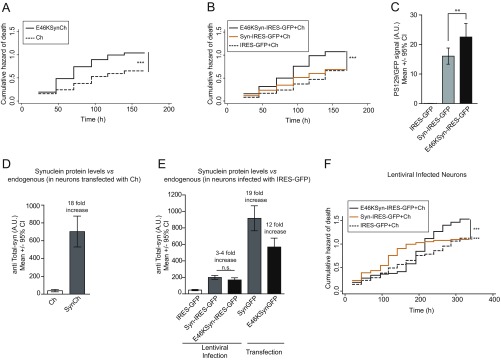
Untagged IRES-GFP versions of aSyn show neuronal toxicity similar to that of Ch-tagged versions. (A) Cumulative hazard estimates of primary rat cortical neurons coexpressing E46KSynCh and Ch as control (n = 250–300 neurons per condition; CPH analysis; ***P < 0.001). (B) Cumulative hazard of death of primary rat cortical neurons coexpressing WT or E46K aSyn (Syn-IRES-GFP, E46KSyn-IRES-GFP) and Ch. Control conditions are neurons coexpressing IRES-GFP and Ch (n = 250–300 neurons per condition; CPH analysis; ***P < 0.001). (C) Quantification of anti-PS129 binding relative to GFP (from IRES-dependent expression) in individual primary rat cortical neurons expressing IRES-GFP, Syn-IRES-GFP, and E46KSyn-IRES-GFP from immunofluorescence experiments (n = 42–66 neurons per condition; one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test; **P < 0.01). All error bars represent 95% CIs. (D) Quantification of total aSyn protein levels in immunostained individual neurons transfected with Ch and SynCh. Total aSyn levels in Ch-transfected neurons are indicative of endogenous aSyn levels (n = 10–12 neurons per condition). (E) Quantification of anti-total aSyn binding in individual neurons infected with lentivirus (IRES-GFP as control, Syn-IRES-GFP, or E46KSyn-IRES-GFP) or transfected with SynGFP and E46KSynGFP. Total aSyn levels in IRES-GFP–infected neurons are indicative of endogenous aSyn levels (n = 20–70 neurons per condition; Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn’s post hoc test). All error bars represent 95% CIs. (F) Longitudinal survival analysis in primary rat cortical neurons infected with aSyn-expressing lentivirus. Cumulative hazard estimates of primary rat cortical neurons transfected with Ch and infected 4 h later with E46KSyn-IRES-GFP, Syn-IRES-GFP, or IRES-GFP, respectively (n = 150–300 neurons per condition; CPH analysis; ***P < 0.001).