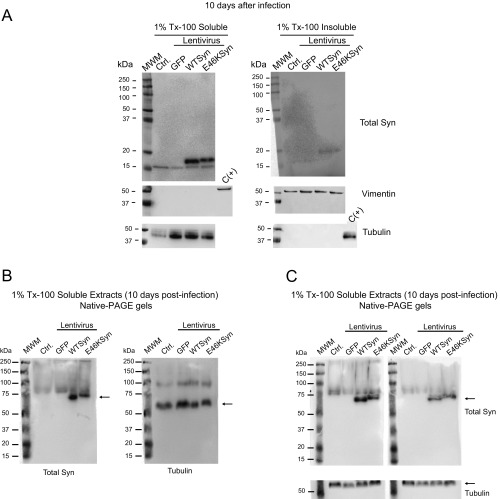
Fig. S4.
The E46K aSyn pathological mutation does not form Tx-100–insoluble aggregates in primary rat cortical neurons 10 d after lentiviral infection. (A) Ten days after lentiviral infection, extracts of primary neuron cultures were homogenized in 1% Tx-100, and the detergent-soluble and -insoluble protein fractions obtained by ultracentrifugation at 100,000 × g were analyzed in Western blots. The aSyn is predominantly detected in the Tx-100–soluble fraction with a mass of ≈16 kDa; as reported, tubulin appears in the soluble fraction, and vimentin appears in the insoluble fraction. A sample from the opposite fraction was used as a positive control [C(+)]. Each experiment was performed twice with similar results. (B) Analysis of 1% Tx-100–soluble fractions from neuronal protein extracts infected with aSyn expressing lentivirus by native PAGE gels and Western blot. Rat cortical primary neurons were infected with lentivirus expressing WT or E46K mutant aSyn. Ten days after lentiviral infection, extracts of primary neuron cultures were homogenized with 1% Tx-100. The detergent-soluble fraction was separated by ultracentrifugation, run in native PAGE gels, and analyzed by Western blot with a specific antibody against Total aSyn. aSyn is detected with an apparent mass between 60–70 kDa. The same membrane was stripped and incubated with anti-tubulin antibody. Tubulin is detected with an apparent mass of 60 kDa. (C) The upper membranes represent two independent replicates of the experiment described in B. These membranes have been cut and incubated with anti-tubulin antibody. Ctrl, control noninfected neurons; MWM, molecular weight marker.